Figure 2.
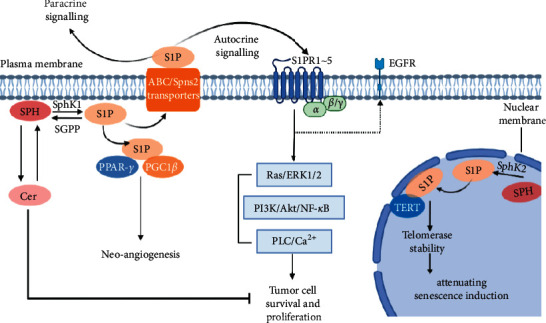
SphK1-generated S1P engages with G protein-coupled S1P receptors (S1PR1–5) to regulate specific cellular functions. S1P also directly associates with PPAR-γ, which then mediates the recruitment of PGC1β to induce neo-angiogenesis. Generation of S1P by SphK2, which is localized in the nuclear membrane, interacts with TERT to stabilize telomerase and attenuate senescence induction. PI3K, phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase; MAPK, mitogen-activated protein kinases; PLC, phospholipase C; PPAR-γ, proliferator-activated receptor-γ; TERT, telomerase reverse transcriptase; EGFR, epidermal growth factor receptor; ERK1/2, extracellular signal-regulated kinases 1 and 2; NF-κB, nuclear factor-κB; PLC, phospholipase C; S1P, sphingosine-1-phosphate; S1PR, sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor; Sph, sphingosine; SphK1, sphingosine kinase 1; ABC, ATP-binding cassette; SPNS2, protein spinster homologue 2.
