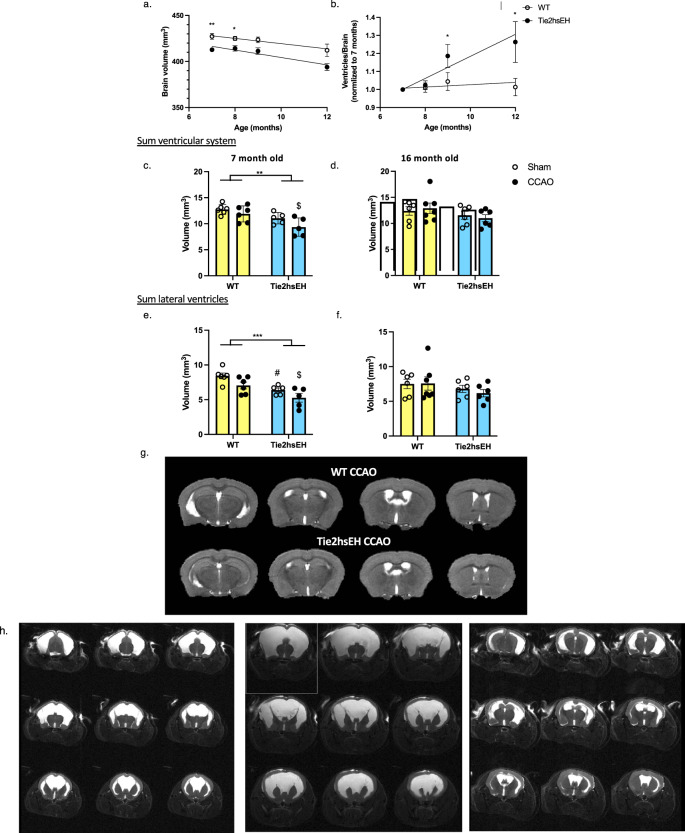
Fig. 4. Age-dependent atrophy and ventriculomegaly in Tie2hsEH mice.
Ventricular and total brain volume were measured by T2-weighted MRI. Longitudinal T2-weighted MRI shows that Tie2hsEH mice have a smaller brain volume than WT at 7 and 8 months of age (a), *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, 2-way ANOVA with Sidak’s multiple comparison test, n = 4–18/group. Ventricle size, normalized to brain volume, increases with age in Tie2hsEH mice, but not WT (b); linear regression analysis shows that the slope of Tie2hsEH is steeper than that of WT (0.06 vs. 0.006, respectively, p = 0.0038), with increased ventricle/brain ratio in Tie2hsEH mice at 9 and 12 months of age, *p < 0.05, 2-way ANOVA with Sidak’s multiple comparison test, n = 3–14/group. Ventricular volume is reduced in Tie2hsEH mice compared to WT, in 7-month-old mice (c), but not in 16-month-old-mice (d); CCAO surgery does not alter ventricle volume in either age group. Lateral ventricles are also reduced in volume in the 7- but not 16-month cohort (e, f); a reduction in volume is also observed by CCAO surgery in the 7- but not 16-month cohort. *p < 0.05, ***p < 0.001, #p < 0.05 WT sham vs. Tie2hsEH sham, $p < 0.05 WT CCAO vs. Tie2hsEH CCAO, 2-way ANOVA with Sidak’s multiple comparison test, n = 5–7/group. Representative sequential T2-weighted image slices are shown of both genotypes at 7 months of age (g). Severe hydrocephalus was observed in 3 out of 18 naïve12-month-old Tie2hsEH mice, but not WT, by ASL-MRI perfusion (n/s Fisher’s exact test); MRI images of the 3 hydrocephalic Tie2hsEH brains (h). Data are represented as mean ± SEM.