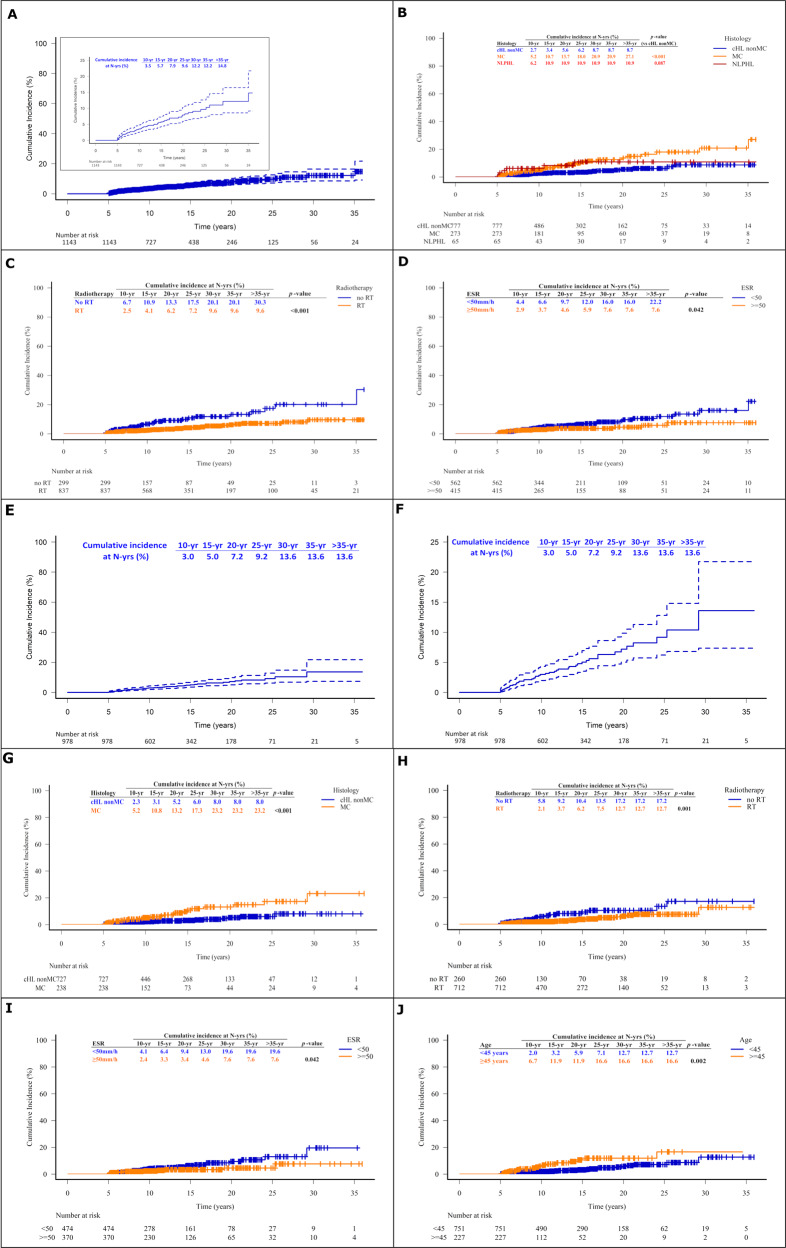
Fig. 1. Cumulative incidence of very late relapses and competing-risks-adjusted cumulative incidence at different time-points from diagnosis in the whole patient population and in individual patients’ subgroups.
Individual graphs refer to the whole patient population overall (A) and according to histologic subtype (cHL classical Hodgkin lymphoma, MC mixed cellularity, NLPHL nodular lymphocyte-predominant Hodgkin lymphoma) (B), radiotherapy (RT) administration (C) and erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) (D). In addition, cumulative incidence of very late relapses and competing-risks-adjusted cumulative incidence at different time-points from diagnosis in patients with classical Hodgkin lymphoma treated with ABVD or equivalent regimens (E, F) and according to histologic subtype (cHL classical Hodgkin lymphoma, MC mixed cellularity) (G), radiotherapy (RT) administration (H), erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) (I) and age (J).