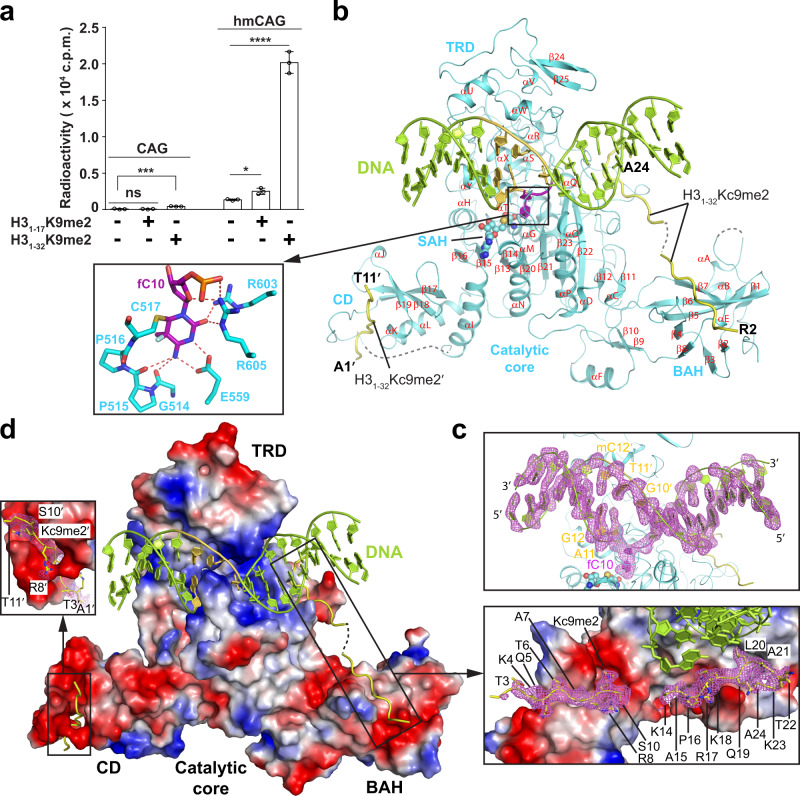
Fig. 1. A structural framework for understanding the H3K9me2-directed CHG methylation maintenance by ZMET2.
a In vitro DNA methylation assay of ZMET2 on an 18-mer DNA duplex containing single CAG or hmCAG site, in the presence or absence of histone peptide (H31–17K9me2 or H31–32K9me2). Data are mean ± s.d. (n = 3 biological replicates). Statistical analysis of the presence vs absence of peptide conditions used two-tailed Student’s t test. ns, not significant; *p = 0.01; ***p = 0.0008; ****p < 0.0001. b Crystal structure of ZMET2 in complex with an 18-mer hmCAG and the H31–32Kc9me2 peptide, with the active site harboring the target cytosine fC10 shown in the expanded view. ZMET2, DNA, and H31–32Kc9me2 peptides are colored in aquamarine, lemon, and yellow, respectively. The hmCAG site is colored in purple (for fC10) or yellow-orange. The SAH molecule is shown in sphere representation. The secondary structures of ZMET2 are labeled numerically for helices and alphabetically for β-strands. The disordered regions of ZMET2 and H3 peptides are depicted as dashed lines. c Fo-Fc omit map (violet; 2.0σ contour) and cartoon representation of the DNA bound to ZMET2, with the nucleotides at the CHG site labeled. d Electrostatic surface view of ZMET2 bound to DNA and H31–32K9me2 peptides, with the Fo-Fc omit maps (violet; 2σ contour) of the H3 peptides (residues labeled; stick representation) are highlighted in the expanded views. The same color scheme in b is applied to all the subsequent figures unless indicated otherwise. Source data are provided as a Source Data file.