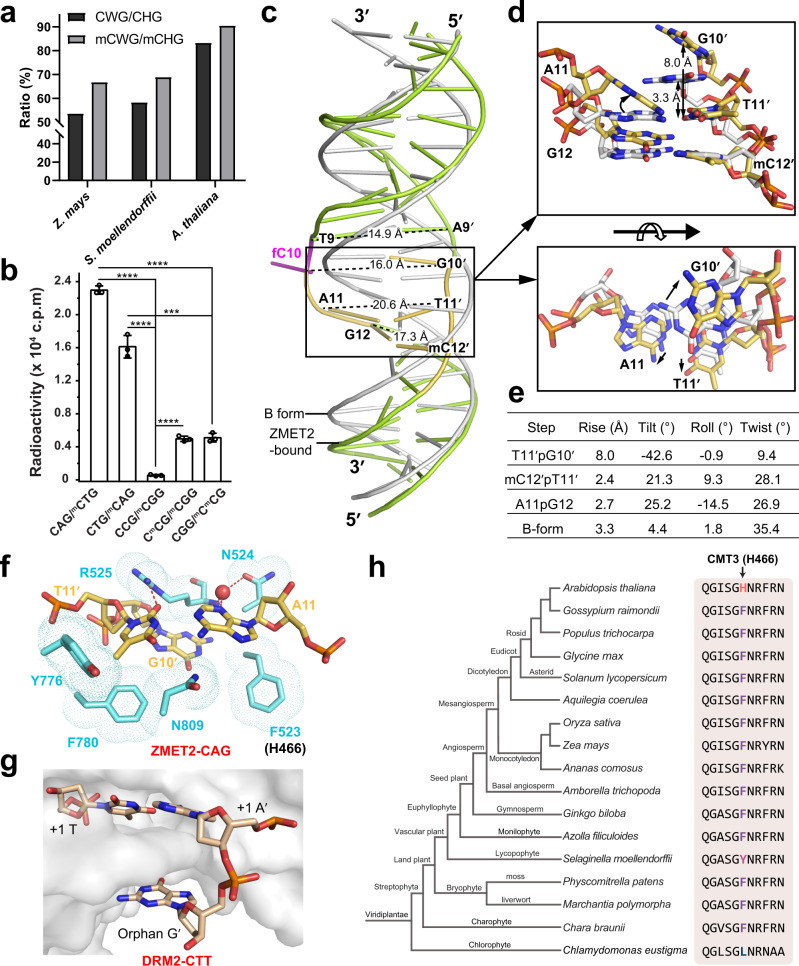
Fig. 4. Substrate deformation underpins the enzymatic preference of CMTs.
a Genome-wide ratio of CWG over all CHG sites and methylated CWG (mCWG) over all methylated CHG (mCHG) sites in three plant species. b In vitro DNA methylation of ZMET2 on CHG DNA with various sub-sequence contexts. Data are mean ± s.d. (n = 3 biological replicates). Statistical analysis used two-tailed Student’s t test. ***p < 0.001; ****p < 0.0001. c Structural overlay of ZMET2-bound 18-mer hmCAG DNA and the B-form DNA (gray) in the same sequence. The inter-strand distances around the CAG site are labeled. d Two orthogonal views highlight structural deviation of the CAG site of the ZMET2-bound DNA from the B-form DNA. The conformational shift is indicated by black arrow. e Geometric parameters for the DNA base steps boxed in (c, d). f Close-up view of the deformed +1-flanking A11·T11′ pair and neighboring orphan G10′ and their protein contacts in the ZMET2-hmCAG-H31–32Kc9me2 complex. The water molecule is shown as a red sphere. The hydrogen bonds are shown as dashed lines. g Close-up view of the CTT DNA bound to DRM2 (PDB 7L4C), highlighting the deformation of the +1-flanking A·T pair. DRM2 is shown in gray surface representation. h Phylogenetic analysis of the DNA-intercalation sequence of CMT3. The CMT3 H466-corresponding site is colored by amino acid identity. Source data are provided as a Source Data file.