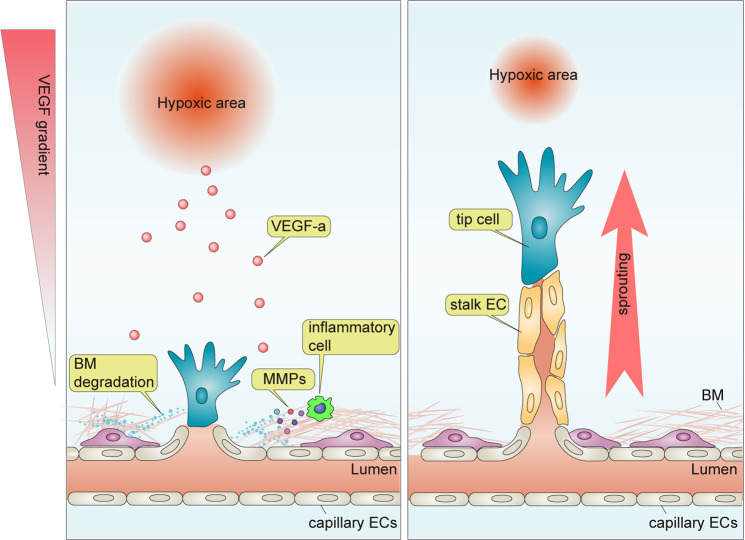
Fig. 1. Traditional model for angiogenesis.
Cells under hypoxia increase the expression of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF-A). This induces vascular stalk formation from the responding capillary bed and stimulates the recruitment of proinflammatory cells, including circulating and tissue-residing macrophages and T cells. The latter is largely responsible for the local production of MMPs that break the extracellular matrix and facilitate endothelial cell migration. Depending on their position in the angiogenic sprout, endothelial cells differentiate into tip or stalk cells. Tip cells at the vascular front sense the VEGF gradient and direct the growing sprout toward its source. Stalk cells follow behind the tip and form an interconnected vascular lumen.