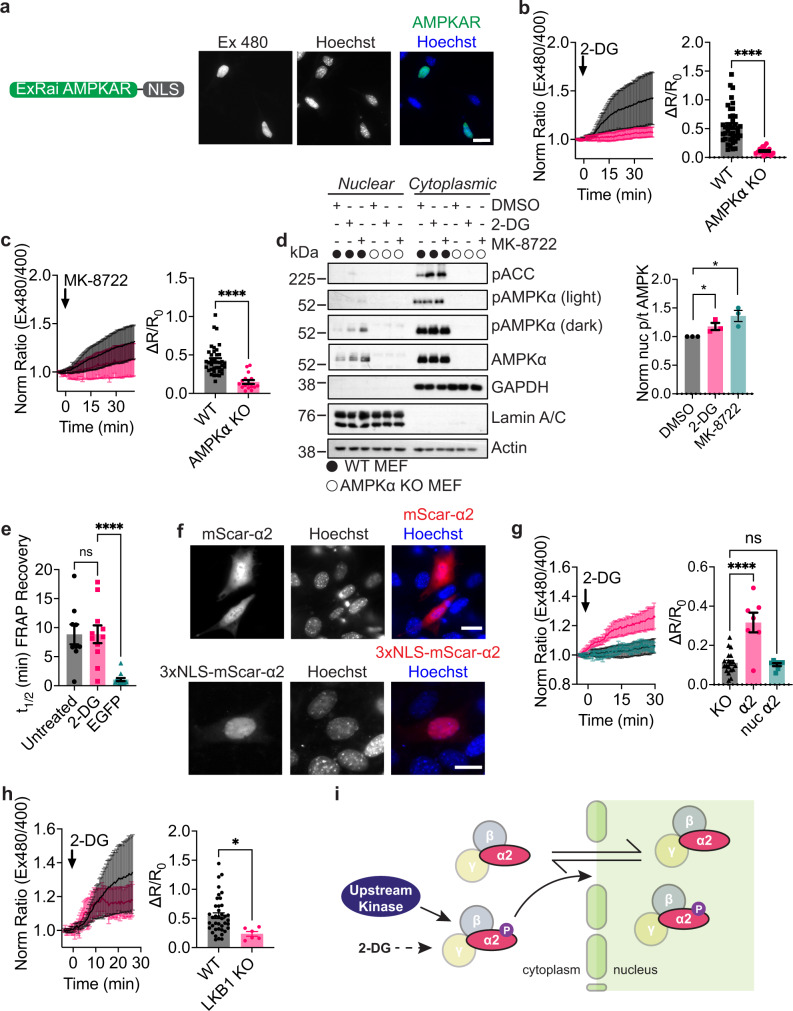
Fig. 4. Nuclear AMPK activity measured using ExRai AMPKAR.
a Domain layout and representative image of ExRai AMPKAR-NLS expressed in MEFs stained with Hoechst nuclear marker. b Average response of ExRai AMPKAR-NLS in either WT (black, n = 46 cells from five experiments) or AMPKα KO MEFs (pink, n = 19 cells from four experiments) treated with 2-DG (40 mM), along with maximum ratio change (****p = 1.51 × 10−7, unpaired t-test, two-tailed). c Average response of ExRai AMPKAR-NLS in either WT (black, n = 38 cells from nine experiments) or AMPKα KO MEFs (pink, n = 16 cells from two experiments) treated with MK-8722 (500 nM), along with maximum ratio change (****p = 6.35 × 10−7, unpaired t-test, two-tailed). d Western blot of nuclear-fractionated MEFs treated with DMSO, 2-DG (40 mM), or MK-8722 (500 nM) for 60 min. Quantification from three independent trials (*p = 0.047 DMSO vs. 2-DG; 0.020 DMSO vs. MK-8722, unpaired t-test, two-tailed). Full blots are shown in Source Data. e Half-time of FRAP recovery (min) for nuclear EGFP-AMPKα2 in AMPKα KO MEFs either without (n = 9 cells from three experiments) or with 2-DG stimulation (40 mM, n = 11 cells from three experiments) immediately before FRAP experiment began, or for EGFP alone (n = 13 cells from two experiments; ns p = 0.999; ****p < 0.0001, one-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s multiple comparisons test). f Representative images of mScarlet-AMPKα2 or 3xNLS-mScarlet-AMPKα2 in MEFs stained with Hoechst nuclear marker. g Average 2-DG (40 mM)-stimulated response of AMPKα KO MEFs expressing ExRai AMPKAR-NLS alone (black, reproduced from b) or co-expressing mScarlet-AMPKα2 (pink, n = 7 cells from two experiments) or 3xNLS-mScarlet-AMPKα2 (teal, n = 8 cells from four experiments), along with maximum ratio change (ns p = 0.96; ****p = 8.67 × 10−7, one-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s multiple comparisons test). h Average response of ExRai AMPKAR-NLS in either WT (black, reproduced from b) or LKB1 KO MEFs (pink, n = 6 cells from four experiments) treated with 2-DG (40 mM), along with maximum ratio change (*p = 0.021, unpaired t-test, two-tailed). i Mechanism of 2-DG-induced nuclear AMPK activity where nuclear AMPK activity in response to 2-DG is initiated in the cytoplasm dependent on upstream kinases, after which AMPK then translocates into the nucleus to phosphorylate nuclear targets. For all figures, time courses show the mean ± SD, dot plots show the mean ± SEM. Scale bars, 20 µm.