Figure 2. BCAT1i and AKG induces synthetic lethality in patient-derived IDHWT GBM.
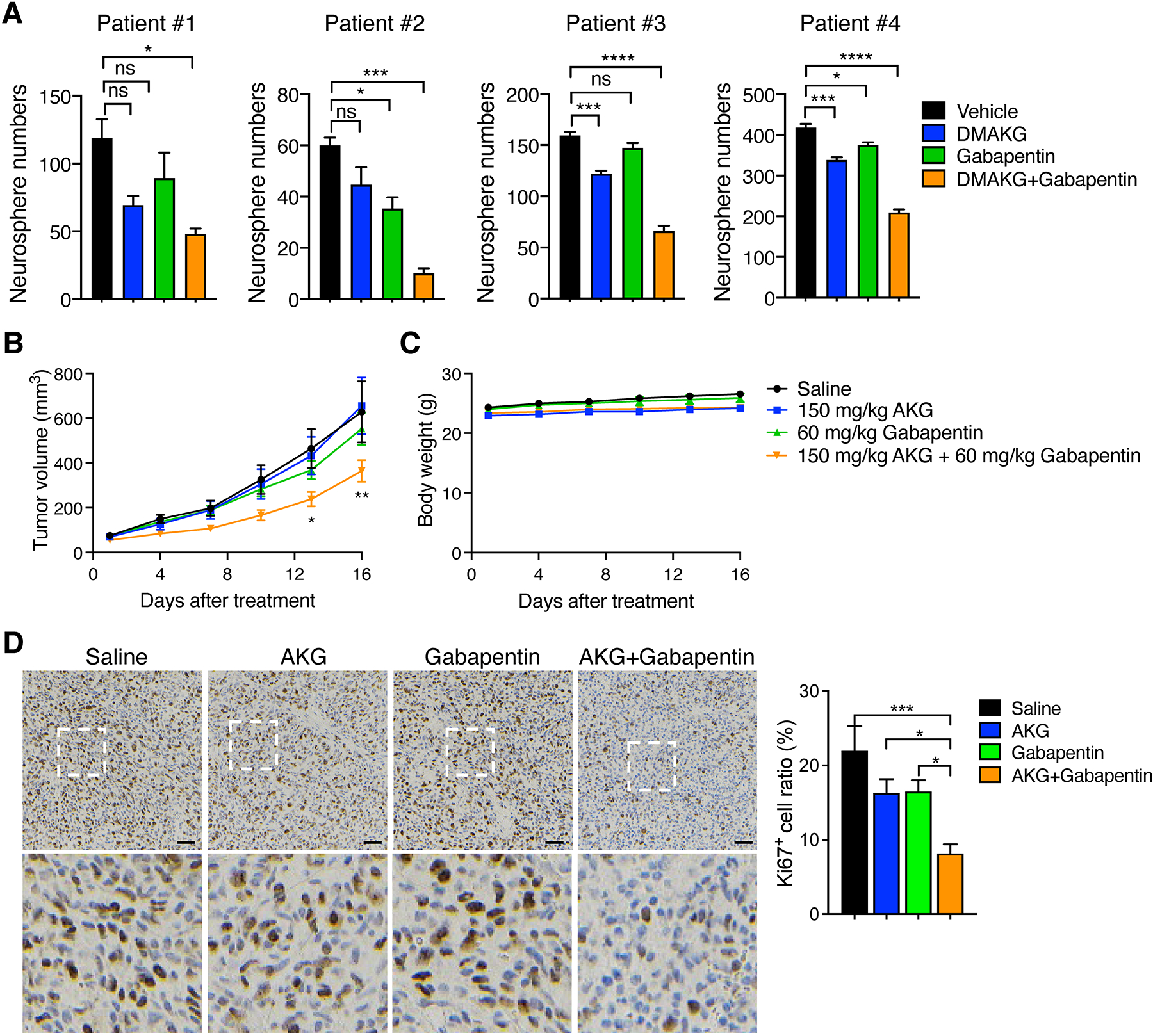
(A) Tumorsphere assay in patient-derived IDHWT GBM treated with vehicle, DMAKG (10 mM), gabapentin (5 mM), or both for 7 days. Tumorspheres with > 50 μm diameter are counted (mean ± SEM, n = 3). ns, not significant. *p < 0.05; ***p < 0.001; ****p < 0.0001 by one-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s test. (B and C) Patient-derived IDHWT GBM xenograft assay. Tumors were treated with saline, AKG, gabapentin, or both for 16 days. The tumor growth curve is shown in B (mean ± SEM, n = 7–9). The mouse body weight is shown in C (mean ± SEM, n = 7–9). *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01 by two-way ANOVA with Tukey’s test. (D) Ki67 immunohistochemical staining in patient-derived IDHWT GBM tumors harvested from xenograft assay. Representative images are shown at the top and magnified images of the boxed area are shown at the bottom. Scale bar, 50 μm. The percentage of Ki67+ cells is quantified at the right (mean ± SEM, n = 7–8). *p < 0.05; ***p < 0.001 by one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s test.
