Figure 6. BCAT1i/AKG causes mTORC1 inactivation and protein depletion in IDHWT GBM cells.
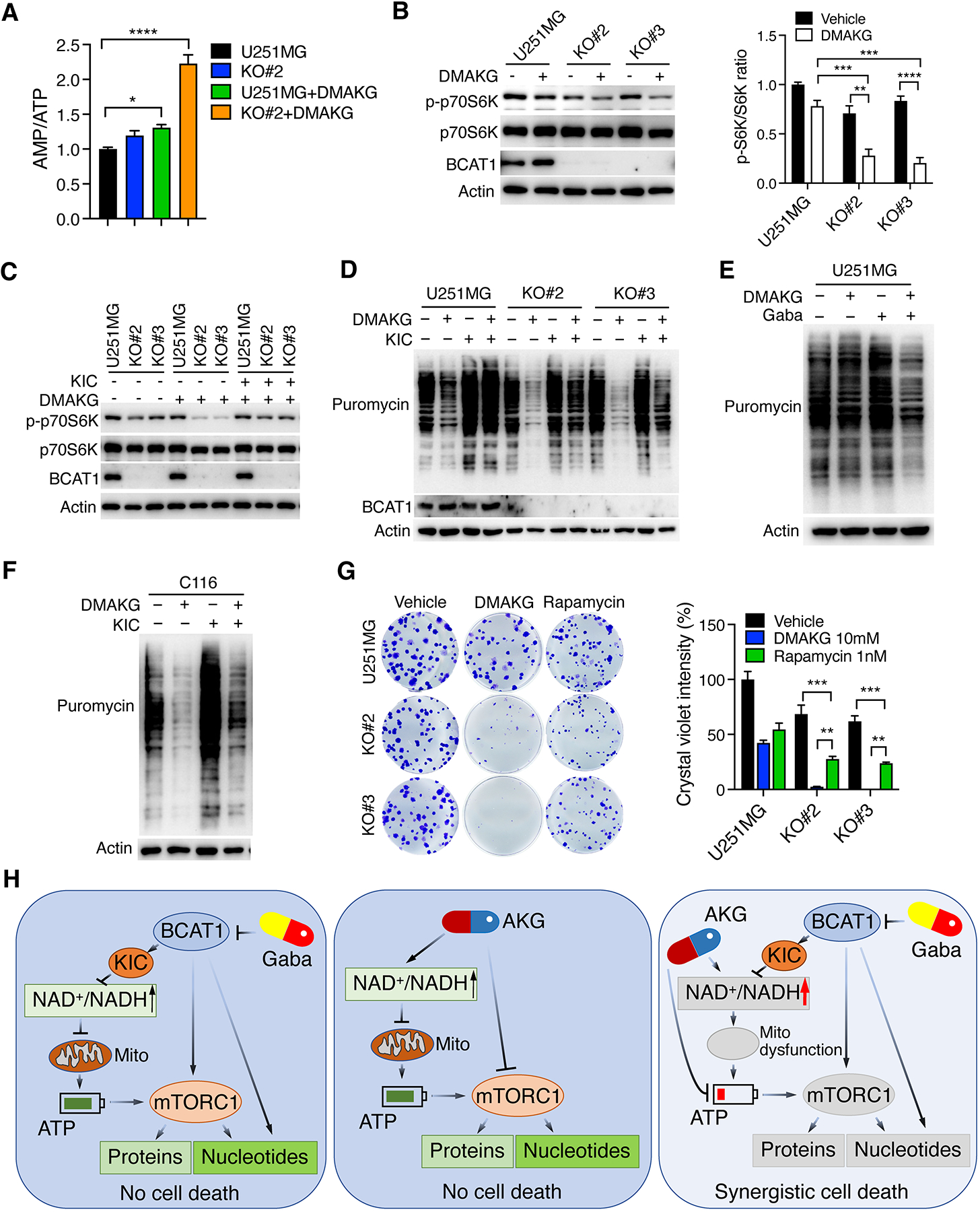
(A) Mass spectrometry analysis of AMP/ATP ratio in parental and BCAT1 KO#2 U251MG cells treated with vehicle or DMAKG (10 mM) for 24 hours (mean ± SEM, n = 5). *p < 0.05; ****p < 0.0001 by one-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s test. (B) Immunoblot analysis of mTORC1 activation in parental and BCAT1 KO#2 or KO#3 U251MG cells treated with vehicle (-) or DMAKG (10 mM) for 24 hours. Representative blots are shown in the left. Intensities of p-p70S6K and p70S6K bands are quantified and their ratio is shown in the right (mean ± SEM, n = 3). **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001; ****p < 0.0001 by two-way ANOVA with Tukey’s test. (C) Immunoblot analysis of mTORC1 activation in parental and BCAT1 KO#2 or KO#3 U251MG cells treated with vehicle (-), DMAKG (10 mM), KIC (1 mM), or both for 24 hours. (D) Analysis of protein synthesis in parental and BCAT1 KO#2 or KO#3 U251MG cells treated with vehicle (-), DMAKG (10 mM), KIC (1 mM), or both for 24 hours. (E) Analysis of protein synthesis in U251MG cells treated with vehicle (-), DMAKG (10 mM), gabapentin (Gaba, 20 mM), or both for 48 hours. (F) Analysis of protein synthesis in C116 cells treated with vehicle (-), DMAKG (10 mM), KIC (1 mM), or both for 24 hours. (G) Clonogenic assay in parental and BCAT1 KO#2 or KO#3 U251MG cells treated with vehicle, DMAKG (10 mM), or Rapamycin (1 nM) for 7 days. Representative images are shown at the left. The intensity of crystal violet is quantified at the right (mean ± SEM, n = 3). **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001 by two-way ANOVA with Tukey’s test. (H) A proposed model of BCAT1i/AKG-induced synthetic lethality in IDHWT GBM. BCAT1 inhibition causes a modest reduction of NADH, ATP, nucleotides, and proteins through loss of BCKAs, nitrogen donor glutamate, and/or mTORC1 activity in IDHWT GBM cells. Likewise, AKG modestly reduces nucleotide biosynthesis and protein synthesis through mTORC1 inhibition, inhibits ATP production, and increases NADH oxidation into NAD+. While BCAT1 loss or AKG alone-induced metabolic alterations are not sufficient to kill cells, BCAT1i/AKG combination has a significant impact on mitochondrial dysfunction and depletion of ATP, nucleotides, and proteins, leading to IDHWT GBM cell death. Gaba, gabapentin. Mito, mitochondrial. All immunoblot data are shown from one of three independent experiments.
