Fig. 3. Site-specific H2B acetylation is elevated in MDA-MB-231 cells expressing H2B-D51 oncohistone mutants.
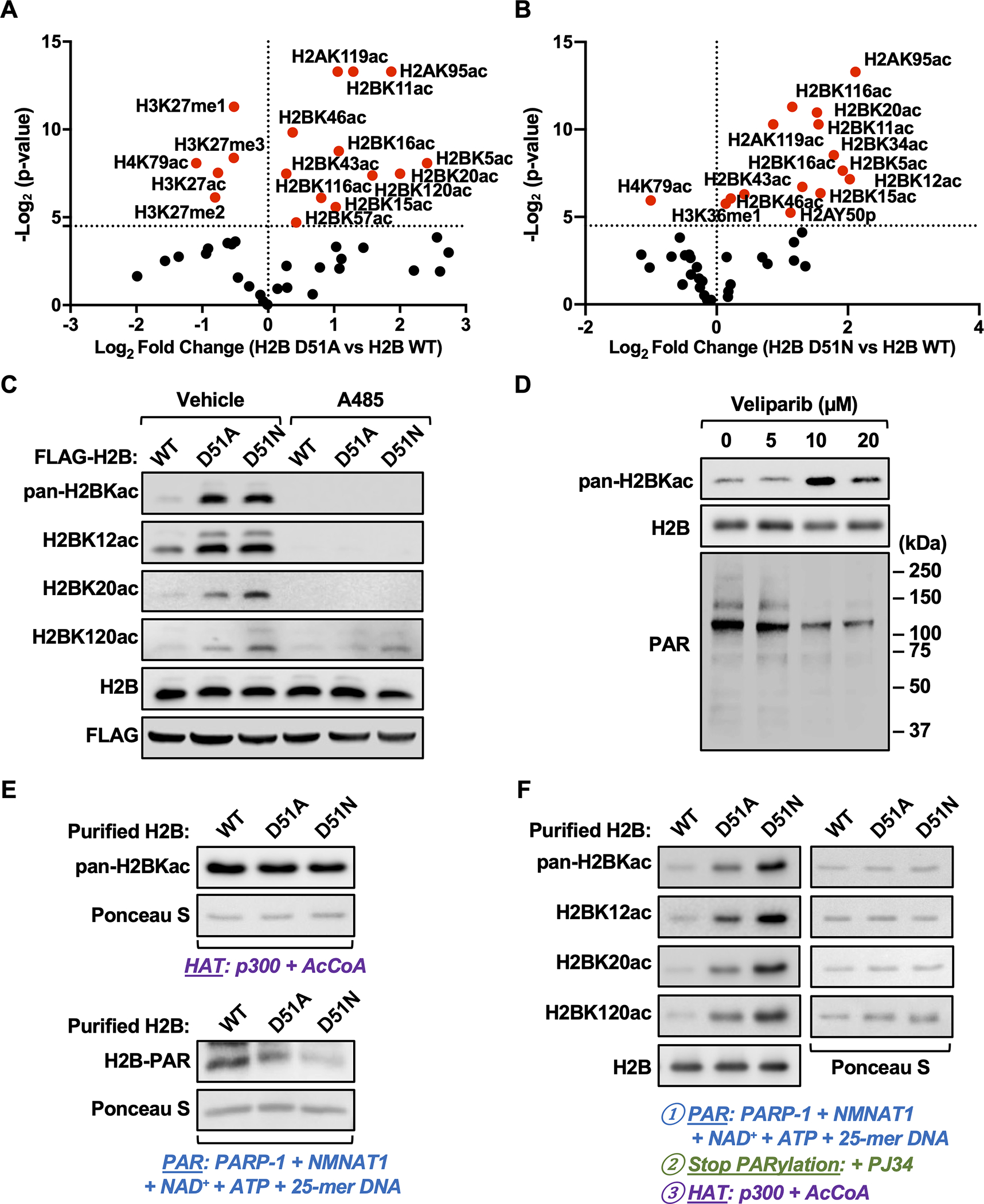
A and B) Quantification of histone modifications by mass spectrometry in MDA-MB-231 cells ectopically expressing FLAG-tagged WT, D51A, or D51N H2B. Volcano plots showing statistical significance (p-value) plotted versus the abundance of modified peptides (fold change of H2B D51 mutant versus H2B WT; D51A, panel A; D51N, panel B) for individual site-specific histone modifications. Points plotted in red indicate histone modifications significantly different in the H2B mutants versus H2B WT (p < 0.05). The data are from three biological replicates of FLAG-tagged nucleosomes from MDA-MB-231 cells enriched by immunoprecipitation after MNase digestion of chromatin analyzed by LC-MS/MS.
C) Western blots showing the levels of pan-H2BKac, H2BK12ac, H2BK20ac, and H2BK120ac in MDA-MB-231 cells ectopically expressing FLAG-tagged WT, D51A, or D51N H2B ± treatment with A485 (5 μM, 2 hours) or vehicle (DMSO).
D) Western blots showing the levels of pan-H2BKac and PAR in MDA-MB-231 cells ± treatment with the PARPi Veliparib (5–20 μM) for 2 hours.
E) In vitro HAT assays were performed using purified H2B (WT, D51A and D51N), p300, and acetyl-CoA (upper panels). In vitro PARylation assays were performed using purified H2B (WT, D51A and D51N), PARP-1, NMNAT-1, NAD+, ATP, and 25-mer DNA (lower panels). Western blots showing the levels of pan-lysine acetylation (upper panels) and PAR (lower panels) on H2B. Ponceau S staining of H2B was used to assess equal loading of material.
F) In vitro PARylation assays with purified H2B (WT, D51A and D51N) were performed as described in (E) and stopped by the addition of the PARPi PJ34, followed by HAT assays with the addition of p300 and acetyl-CoA. Western blots showing the levels of pan-H2BKac, H2BK12ac, H2BK20ac, and H2BK120ac. Blots for H2B (left bottom panel) and Ponceau S staining of H2B (right panels) were used to assess equal loading of material.
[See also Supplementary Fig. S9 and Supplementary Data S2]
