Figure 1. Structural insights into the potent trapping of TOP1ccs by exatecan.
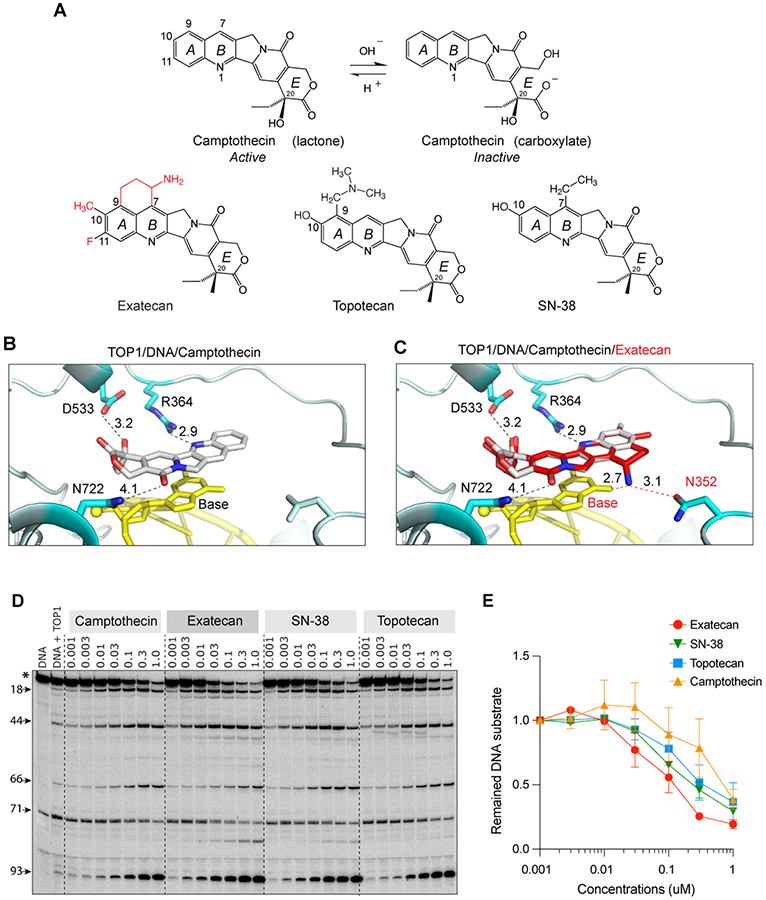
A. Chemical structures of CPT and its clinical derivatives (exatecan, topotecan, and SN-38). B. Representative view of CPT (light grey) bound to human TOP1 (cyan) and DNA (yellow) (PDB: 1T8I). In addition to base stacking, CPT makes 3 hydrogen bonds with TOP1 through D533, N722 and R364. The numbers indicate the distance of the bonds in Angstrom. C. Superposition of exatecan (red) and CPT (light grey) into the TOP1 (cyan)-DNA (yellow) structure. The 2 dotted lines (red) represent the potential additional hydrogen bonds of exatecan with the DNA base and N352 of TOP1. D. Comparative TOP1-mediated DNA cleavage (TOP1ccs) induced by exatecan and other TOP1 inhibitors. Recombinant TOP1 was incubated with 3'-end labeled 117 bp DNA oligo in the presence of the indicated drug concentrations. Fragmented DNA oligos were visualized on PAGE gel by using PhosphorImager (Molecular Dynamics). E. Quantitation of DNA substrates (*) as shown in panel D in duplicate experiments. The band intensity was determined by Image Quant software (Molecular Dynamics).
