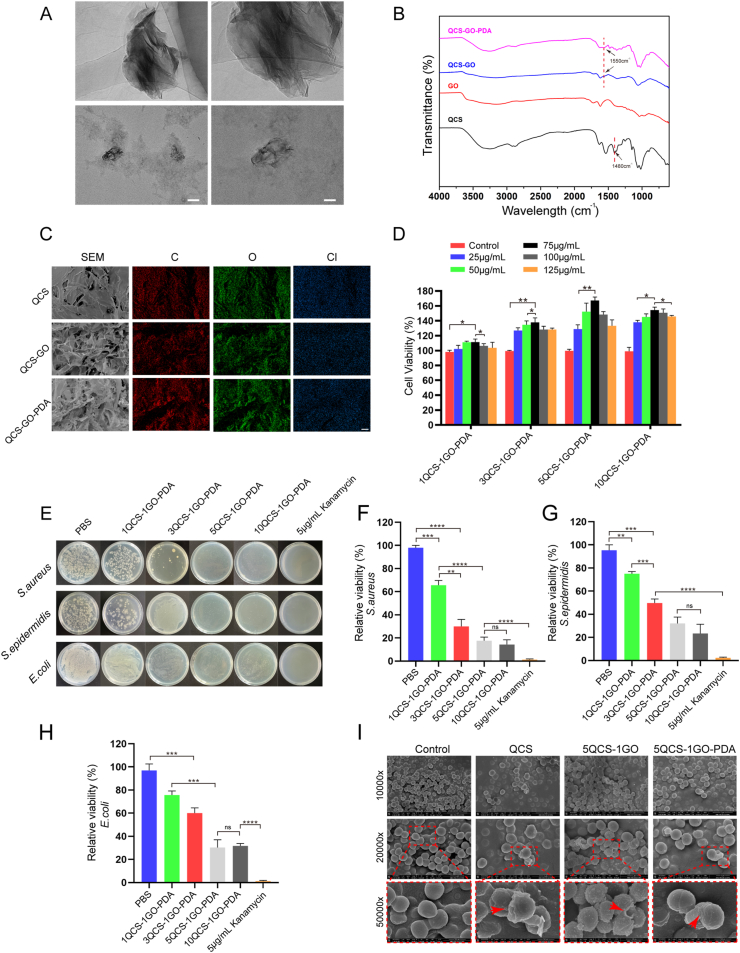
Fig. 1.
Characterization of the nanohybrids and screening of high cell viability and strong antibacterial effects. (A) Representative TEM images of the QCS-GO-PDA. Scale bar: 200 nm (left) and 100 nm (right). (B) FTIR of QCS/GO/QCS-GO/QCS-GO-PDA. (C) SEM and EDS mapping after freeze drying of QCS, QCS-GO and QCS-GO-PDA. Scale bar: 50 μm. (D) Cell viability analysis of QCS-GO-PDA containing different proportions of QCS/GO. (E–H) Representative images and quantitative analysis of antibacterial ability of the different proportions of QCS-GO-PDA (S. aureus, S. epidermidis and E. coli). (I) After being treated with QCS, 5QCS-1GO and 5QCS-1GO-PDA for 2 h, the morphological changes of S. aureus were observed. Scale bar: 3 μm (top), 1 μm (middle) and 500 nm (bottom). Data are represented as mean ± SD (n = 3, *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, ****p < 0.0001).