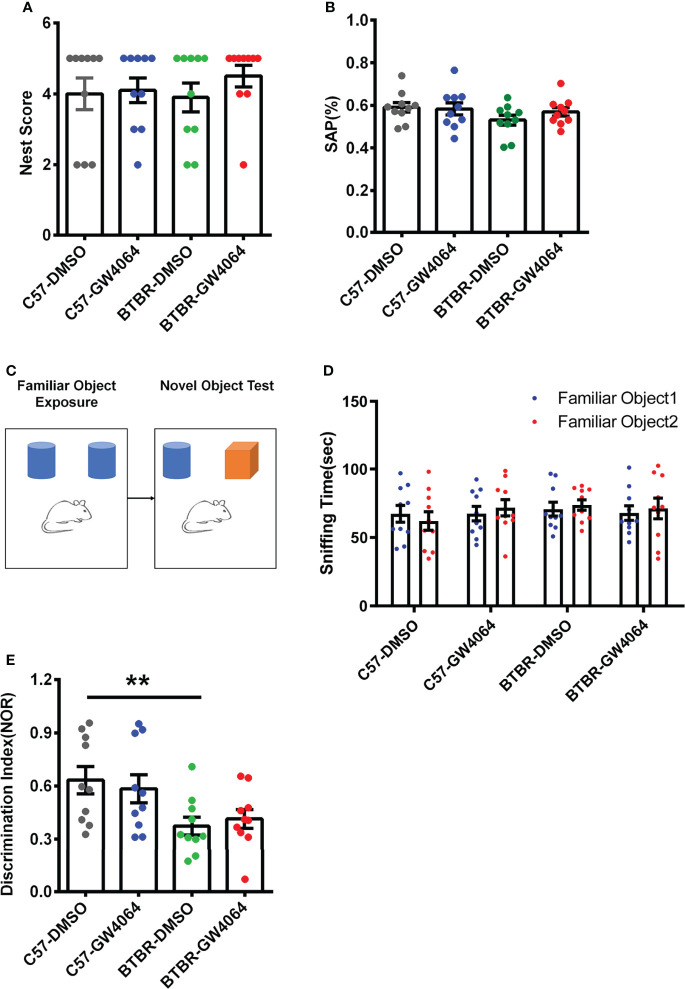
Figure 3.
GW4064 treatment did not alter performance in the nest building and Y-maze tests and did not rescue short-term memory deficits in BTBR mice. (A, B) GW4064 treatment did not alter the nest scores in the nest building and the percentage of SAP in the Y-maze test. (C) Schematic illustration of the new object recognition task. After a period of exposure, one of the two familiar objects is replaced by another unfamiliar one, then test the time the mice stay with the novel object and the familiar object. (D) The sniffing time of new object recognition has no obvious preference between the familiar object 1 and the familiar object 2 during the initial learning phase. (E) BTBR mice displayed a lower discrimination index than C57 mice, which were not rescued by GW4064 treatment. The data are presented as the mean ± SEM. n = 10. **p < 0.01.