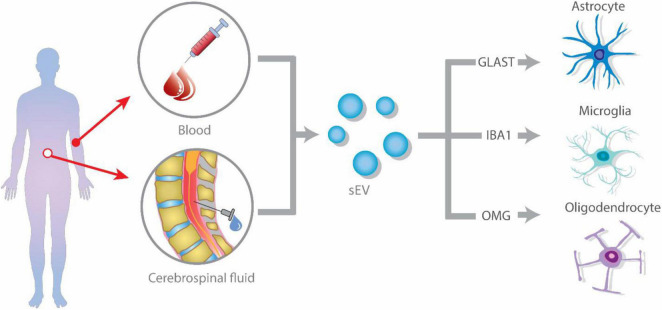
FIGURE 1.
Glial-derived exosomes isolation strategies from blood or plasma. Extracellular vesicles (EVs) are released by glial cells, containing different cargo molecules such as cytokines, proteins, and non-coding RNA. The ability of EVs to cross the blood–brain barrier (BBB), allows them to enter the peripheral blood and cerebrospinal fluid (CSF). Isolation of glial cell-derived exosomes from blood or CSF is accomplished by identifying glial-specific proteins surface markers, such as glutamate aspartate transporter (GLAST) for astrocytes, CD11b and isolectin B4 (IB4) for microglia, and oligodendrocyte-myelin glycoprotein (OMG) for oligodendrocytes.