FIGURE 4.
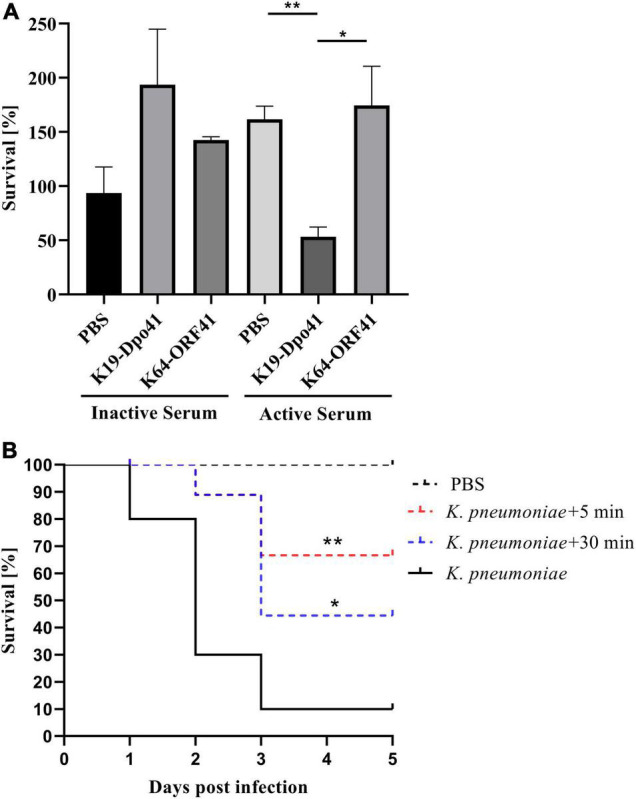
Anti-k. pneumoniae infection effect of K19-Dpo41. (A) Effect of K19-Dpo41 on bacterial susceptibility to serum killing. K. pneumoniae strain 6570 treated with K19-Dpo41 were incubated with active or heat-inactivated human serum obtained from healthy volunteers for 1 h at 37°C. A control group with no K19-Dpo41 was included. A specificity group with K64-ORF41, another depolymerase specifically targeting the CPS of K64-type K. pneumoniae, was also included. The survival rate was defined as the average percent survival of bacteria relative to the initial population. The experiment was repeated three times. Error bars represent mean ± SD. The individual survival rates of each group were compared by Student’s t test. **P < 0.01, *P < 0.05. (B) Effect of K19-Dpo41 on larvae survival rate in a Galleria mellonella larvae infection model. Black solid line, Larvae injected with 5 × 104 CFUs K. pneumoniae strain 6570; red dotted line, K19-Dpo41 (final concentration, 2 μg per larva) administered 5 min after 5 × 104 CFUs K. pneumoniae strain 6570 inoculation; blue dotted line, K19-Dpo41 (final concentration, 2 μg per larva) administered 30 min after 5 × 104 CFUs K. pneumoniae strain 6570 inoculation; black dotted line, Larvae injected with PBS. The mortality were monitored for 5 days (n = 10). Results are the means of three independent experiments. Survival curves were plotted using the Kaplan–Meier method, and differences in survival were calculated by using the log-rank test (GraphPad). **P<0.01 and *p<0.05, mean a significant difference to the K. pneumoniae strain 6570 infected group.
