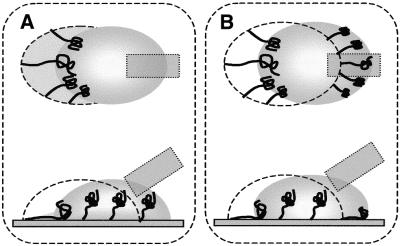
Figure 9.
Behavior of DNAs straightened by droplet motion dependent on surface characteristics. Dotted lines represent the location of the preceding interface in which the extremities of the DNAs have been adsorbed on the surface and solid entangled lines represent stretching DNAs. Gray areas are those wetted by the droplet or soaked in DNA solution. The upper figures are top views of droplet movement and the lower ones side views. (A) Straightening DNAs on a poorly hydrophobic surface. Fixation of the contours of the DNAs, in accordance with their stretching, occurs solely at the receding edge since no fixation is allowed to occur in the wetted areas. (B) Straightening on a highly hydrophobic surface. Fixation occurs at both the advancing and receding edges of the droplet since water repulsion promotes fixation at the advancing edge.