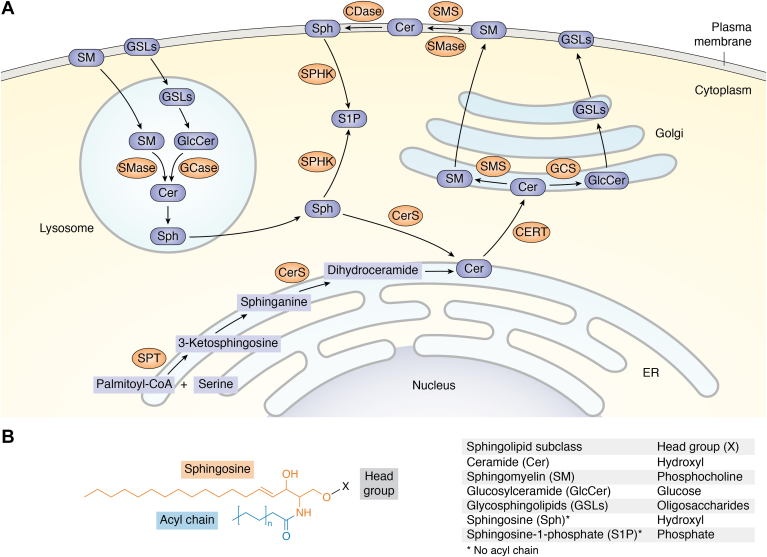
Figure 1.
Compartmentalization of sphingolipid metabolism.A, Cer is initially synthesized in the ER via the de novo synthesis pathway catalyzed by enzymes including SPT and CerS. After transport to the Golgi complex, it is further converted to SM and GlcCer by the enzymes SMS and GCS, respectively. GlcCer is then converted to other complex GSLs by adding additional carbohydrate groups. SM and GSLs are delivered to plasma membranes via vesicular transport. For breakdown, SM and GSLs are transported to lysosomes, where they are degraded to Cer by the actions of enzymes such as SMase and GCase. Cer is further degraded to Sph that is released to the cytoplasm for producing Cer and S1P. B, the structures of the sphingolipid subclasses. CDase, ceramidase; Cer, ceramide; CERT, ceramide transfer protein; CerS, ceramide synthase; ER, endoplasmic reticulum; GCase, glucosylceramidase; GCS, glucosylceramide synthase; GlcCer, glucosylceramide; GSL, glycosphingolipid; SM, sphingomyelin; SMS, sphingomyelin synthase; SMase, sphingomyelinase; S1P, sphingosine-1-phosphate; Sph, sphingosine; SPHK, sphingosine kinase; SPT, serine palmitoyltransferase.