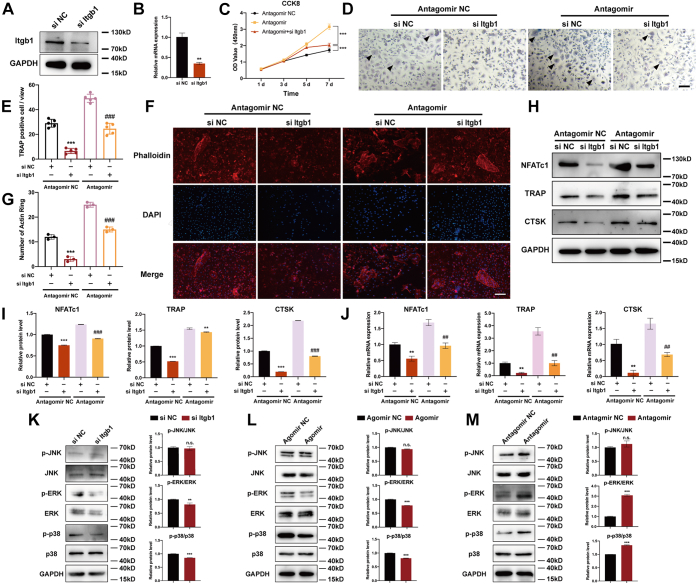
Figure 7.
miR-134-5p suppresses osteoclast differentiation by targeting Itgb1.A and B, BMMs were transfected with si Itgb1 or si NC, and the transfection efficacy was measured by Western blot and qRT-PCR. C, the cell viability of BMMs transfected with antagomir or its control along with si Itgb1 was determined by CCK-8 assay and measured under a microplate reader. D and E, BMMs were transfected with si Itgb1 or its negative control, subjected to antagomir or antagomir NC transfection, and then induced to differentiate into osteoclasts. The number of TRAP-positive multinuclear osteoclasts was counted via TRAP staining. The scale bars represent 100 μm. F and G, transfected BMMs were induced to differentiate into osteoclasts and stained with phalloidin. The number of F-actin rings per field was counted. The scale bars represent100 μm. H and I, the protein expression levels of TRAP, CTSK, and NFATc1 were determined by Western blot. The semiquantitative analysis of the protein expression levels of TRAP, CTSK, and NFATc1 is shown. GAPDH was used as an internal reference control. J, the mRNA expression levels of TRAP, CTSK, and NFATc1 in transfected BMMs were analyzed by quantitative RT-PCR. β-Actin was used as an internal reference gene. K–M, the protein expression levels of the phosphorylated of p38, ERK, and JNK among si Itgb1, agomir, and antagomir groups were determined by Western blot. Semiquantitative analysis of the p-p38/p38, p-ERK/ERK, and p-JNK/JNK ratios was shown. GAPDH was used as an internal reference control. All the data are expressed as the means ± SD. ∗∗p < 0.01 and ∗∗∗p < 0.001 compared with the antagomir NC+si NC group; ##p < 0.01 and ###p < 0.001 compared with the antagomir+si NC group. BMMs, bone marrow macrophages; CCK-8, cell counting kit-8.