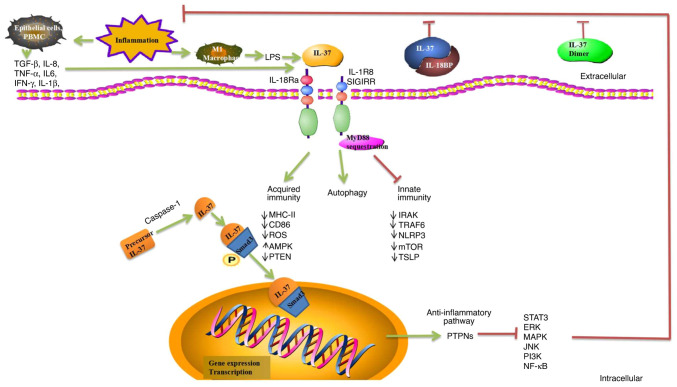
Figure 1.
Role of IL-37 regulation of immunity. IL-37 has significant anti-inflammatory, anticancer, immuno-suppressive, and metabolic regulatory effects. IL-37 binds to IL-18Ra or IL-18BP, which can enhance inhibition of IL-18 and reduce inflammation. The homodimer of IL-37 is a negative regulator of extracellular anti-inflammatory activity. IL-37 is translocated to the nucleus after being processed by caspase-1, and precursor IL-37 is processed into mature IL-37. Complexes formed by mature IL-37 and phosphorylated activated Smad3 in the cytoplasm undergo nuclear translocation into the nucleus, where they play a role in regulating transcriptional activity. PTPNs are activated and numerous related inflammatory and immune pathways are inhibited, including ERK, MAPK, JNK, PI3K, NF-κB, and STAT3. IL-37 binds to its receptor IL-18Rα, recruiting the co-receptor IL-1R8 to form the IL-37/IL-18Rα/IL-1R8 complex at the plasma membrane induced by inhibiting MyD88-dependent signaling. IL-37 negatively regulates inflammatory responses in the innate and acquired immune system by downregulating IRAK, PTEN, ROS, TRAF6, NLRP3, mTOR, TSLP, MHC-II, and CD86. IL-37 acts as an anti-inflammatory cytokine by decreasing the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines and chemokines. IL-37 enhances autophagy and induces metabolic reprogramming by reducing the expression of mTOR and increasing the AMPK levels. However, molecular mechanisms of IL-37-mediated autophagy remain unknown. IL-18Ra, α-subunit of IL-18 receptor; IL-18BP, IL-18 binding protein; PTPNs, protein tyrosine phosphatases; ERK, extracellular signal-regulated kinase; MAPK, mitogen-activated protein kinase; JNK, c-Jun N-terminal kinase; PI3K, phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase; NF-κB, nuclear factor-κB; STAT, signal transduction and activator of transcription; MyD88, myeloid differentiation factor 88; IRAK, interleukin-1 receptor-associated kinase 1; PTEN, phosphatase and tensin homolog; ROS, reactive oxygen species; TRAF6, TNF receptor-associated factor 6; NLRP3, NOD-like receptor family pyrin domain containing 3; mTOR, mammalian target of rapamycin; TSLP, thymic stromal lymphopoietin; AMPK, AMP-dependent protein kinase.