Figure 1.
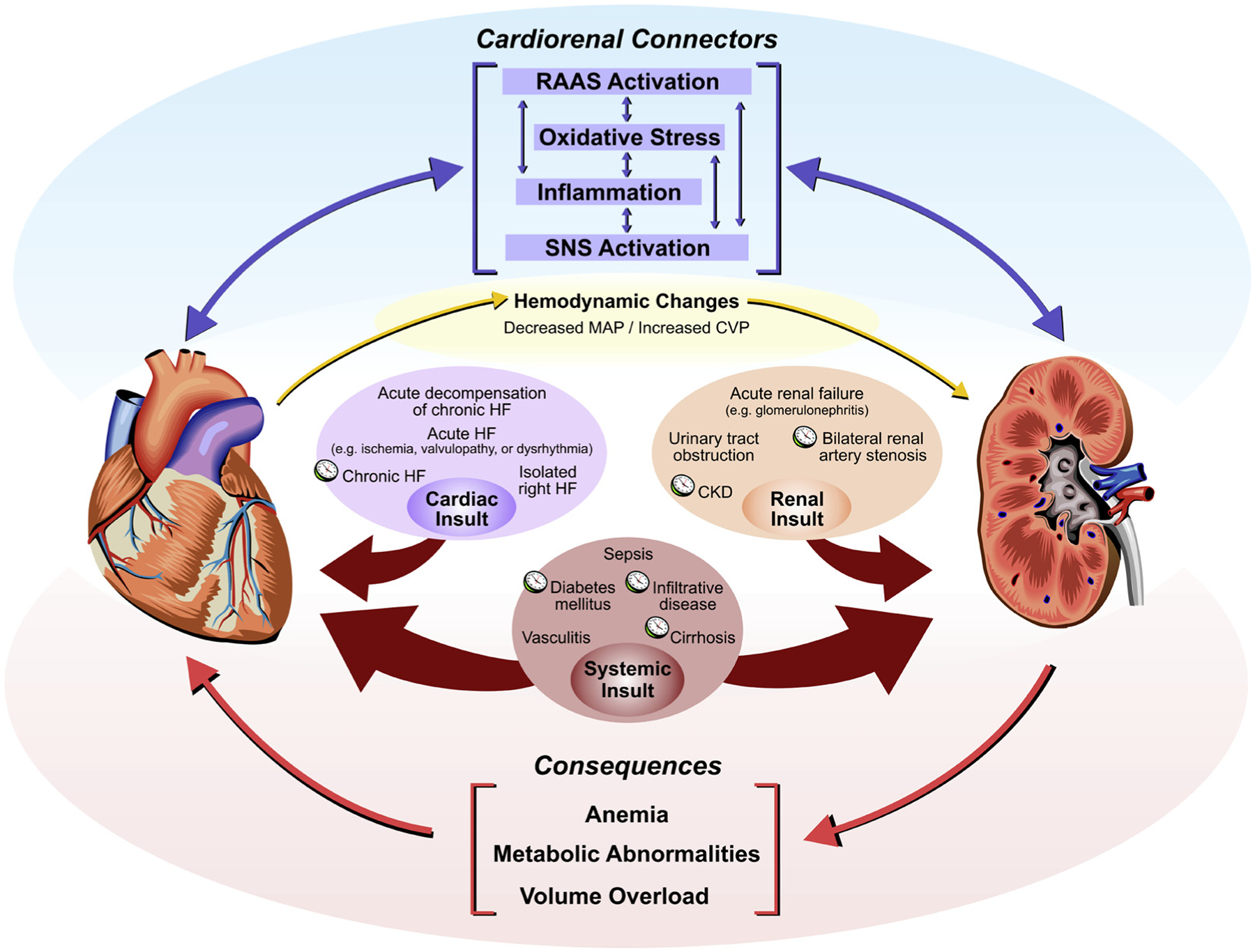
A schematic depiction of the cardiorenal syndrome. Cardiac, renal, or systemic insults result in dysfunction of the heart and/or kidneys. Clocks are used to denote conditions that typically present chronically. The cardiorenal connectors mediate cross-talk between the heart and the kidneys, causing concomitant organ dysfunction. Cardiac dysfunction results in hemodynamic changes, which results in renal dysfunction. The consequences of cardiorenal syndrome include anemia, metabolic abnormalities, and volume overload. CKD, chronic kidney disease; CVP, central venous pressure; HF, heart failure; MAP, mean arterial pressure; RAAS, renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system; SNS, sympathetic nervous system.
