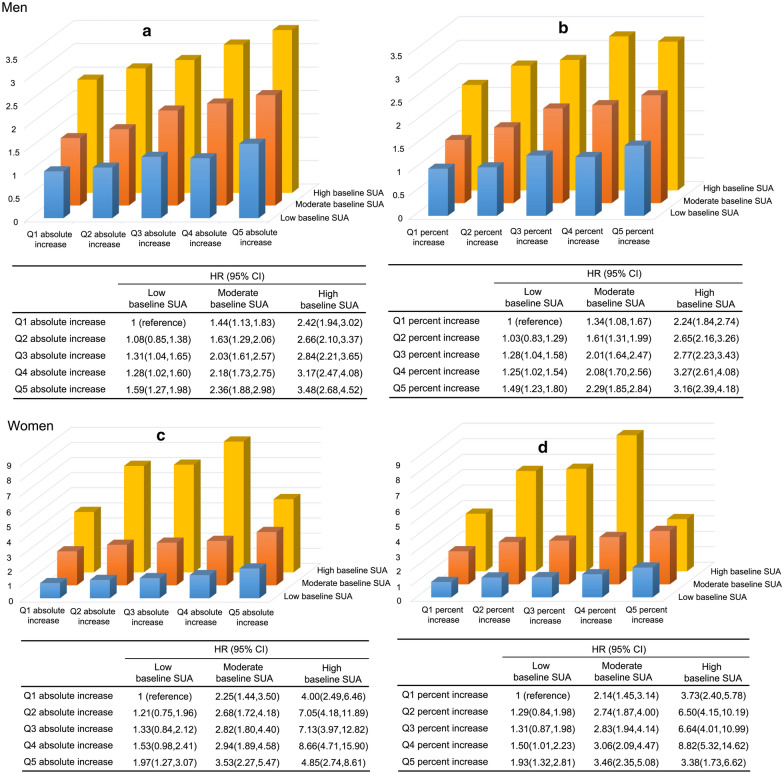
Fig. 2.
Joint associations of baseline SUA levels and longitudinal changes in SUA levels with incident MetS. a SUA longitudinal absolute changes in men. b SUA longitudinal percent changes in men. c SUA longitudinal absolute changes in women. d SUA longitudinal percent changes in women. HR hazard ratio, CI confidence interval. Baseline SUA group: men (< − 360 μmol/L, 360 to < 420 μmol/L, ≥ 420 μmol/L); women (< − 260 μmol/L, 260 to < 360 μmol/L, ≥ 360 μmol/L). Cut-off values of quintiles of SUA absolute changes: men (< − 32 μmol/L, − 32 to < − 6 μmol/L, − 6 to < 15 μmol/L, 15 to < 42 μmol/L, ≥ 42 μmol/L); women (< − 28 μmol/L, − 28 to < − 5 μmol/L, − 5 to < 14 μmol/L, 14 to < 37 μmol/L, ≥ 37 μmol/L). Cut-off values of quintiles of SUA percent changes: men (< − 8.39%, − 8.39% to < − 1.77%, − 1.77% to < 4.36%, 4.36% to < 12.14%, ≥ 12.14%); women (< − 10.19%, − 10.19% to < − 1.90%, − 1.90% to < 5.75%, 5.75% to < 15.29%, ≥ 15.29%). The analysis adjusted for baseline age (continuous, years), smoking status (yes and no), drinking status (yes and no), TC (mmol/L), LDL-C (mmol/L) and SCr (μmol/L)