Figure 4.
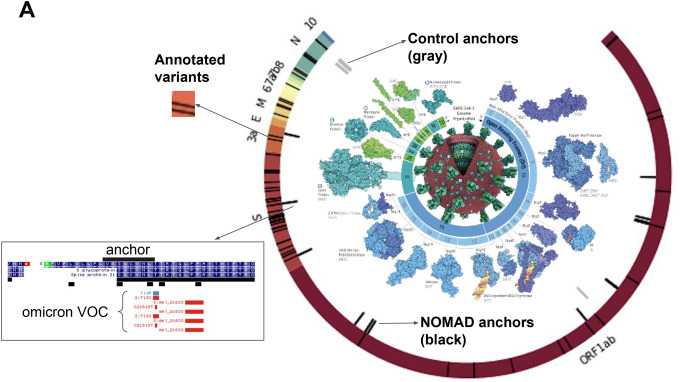
A. Highest effect size NOMAD anchors for SARS-CoV2 (L) that map with bowtie to the Wuhan reference (NC_045512) are shown; enrichment near variants of concern, including a sequence immediately adjacent to one of NOMAD’s called anchors. SARS-CoV2 genome depicted with annotated ORFs and lines depicting positions of variants of concern (VOC) annotated as Omicron and Delta variants. No control anchor maps to spike or other areas of VOC density except in N (nucleocapsid). Protein graphics from https://pdb101.rcsb.org/browse/coronavirus. Data from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sra/SRX14565486[accn.
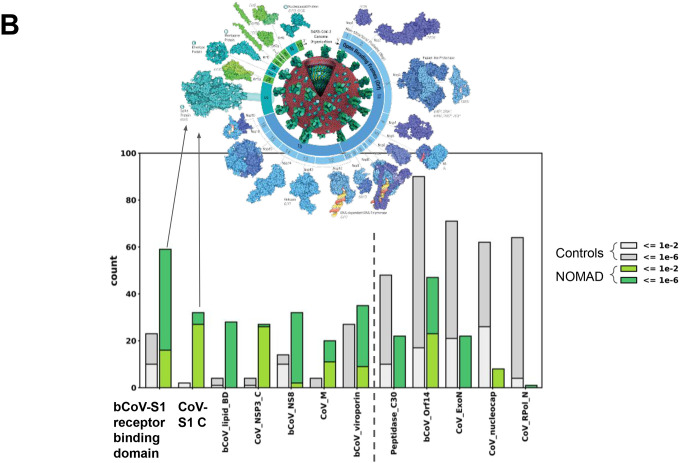
B. NOMAD SARS-CoV2 protein profile hits to the Pfam database (greens) and control (greys); ordered by enrichment in NOMAD hits compared to control. Spike protein domains are highly enriched in the NOMAD hit list (L), the receptor binding domain being highest. NOMAD hits to the CoV spike have higher E-values, suggesting mutations with respect to the reference. The most highly enriched hit is the betacoronavirus S1 glycoprotein receptor binding domain (bCoV_S1_RBD), followed by the spike glycoprotein C-terminal domain (CoV_S1_C), the ORF9b betacoronavirus lipid binding domain (bCoV-lipid_BD), and the coronavirus nonstructural protein 3 replicase C-terminal domain (CoV_NSP3_C). CoV_S1_C and CoV_NSP3_C hits have high E-value hits, potentially explained by an evolutionary divergence from the Pfam entry, predicted if NOMAD were detecting unannotated variants in the SARS-CoV-2 genome. Data from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sra/SRX14565486[accn. Protein graphics from https://pdb101.rcsb.org/browse/coronavirus. Plot was truncated for clarity of presentation as indicated by dashed grey line (Supplement).
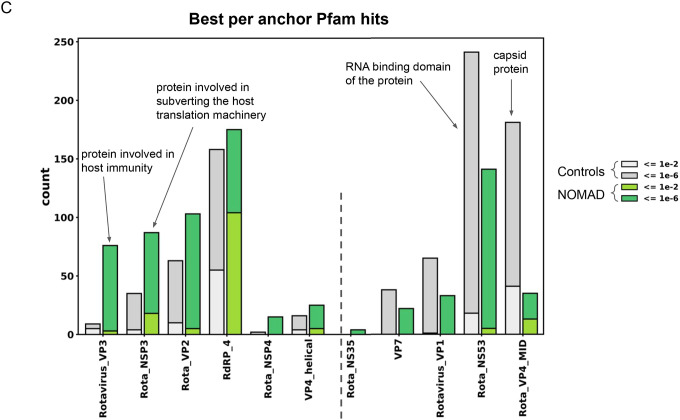
C. NOMAD protein profiles for Rotavirus metagenomic study PRJNA729919: NOMAD protein profile hits to the Pfam database (greens) and control (greys); ordered by enrichment in NOMAD hits compared to control. The most enriched domain is the rotavirus VP3 (Rotavirus_VP3, 76 NOMAD hits vs 9 control hits), a viral protein known to be involved in host immune suppression, followed by the rotavirus NSP3 (Rota_NSP3, 87 NOMAD vs 35 control hits), a viral protein involved in subverting the host translation machinery (77), both proteins that might be expected to be under constant selection given their intimate host interaction. Most enriched in the control: Rota_VP4_MID, an outer capsid coat protein, and RotaNS53, an RNA binding domain of the protein. Plot was truncated for clarity of presentation as indicated by dashed grey line (Supplement).