Figure 3: Detection of differentially regulated alternative splicing and isoforms from single cell RNA-seq.
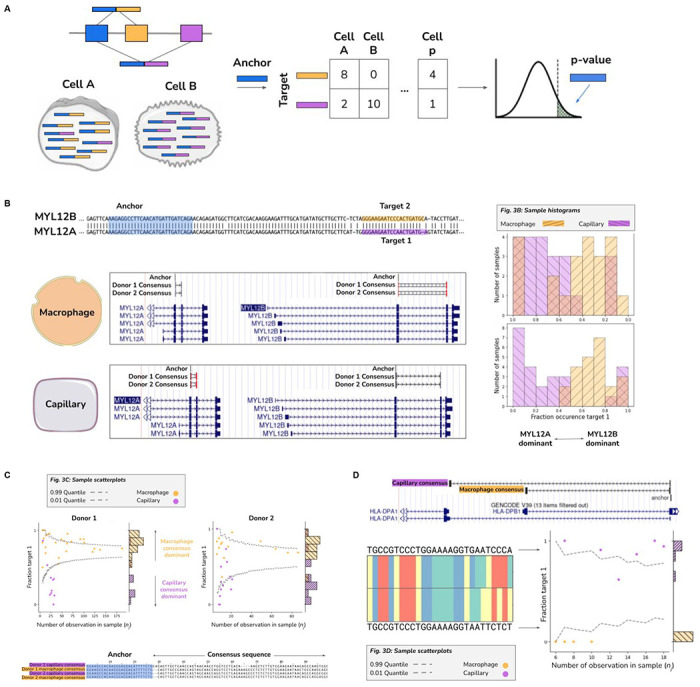
A. Stylized diagram depicting differentially regulated alternative splicing detection with 3 exons and 2 isoforms with NOMAD. Isoform 1 consists of exon 1 (blue) and exon 2 (orange), and is predominantly expressed in cell A. Isoform 2 consists of exon 1 (blue) and exon 3 (purple) and is primarily expressed in cell B.. An anchor sequence in exon 1 (blue), then generates target sequences in exon 2 (orange) or exon 3 (purple). Counts are used to generate a contingency table, and NOMAD’s statistical inference detects this differentially regulated alternative splicing.
B. Detection of differential regulation of MYL12A/B isoforms. (top-left) Shared anchor (q-value 2.5E-8, donor 1, 2.3E-42 for donor 2) highlighted in yellow, maps post fact to both MYL12 isoforms, highlighting the power of NOMAD inference: MYL12A and MYL12B isoforms share >95% nucleotide identity in coding regions. (bottom-left) NOMAD’s approach automatically detects target and consensus sequences that unambiguously distinguish the two isoforms. (right) In both donors, NOMAD reveals differential regulation of MYL12A and MYL12B in capillary cells (MYL12A dominant) and macrophages (MYL12B dominant).
C. NOMAD identifies single-cell-type regulated expression of HLA-DRB1 alleles. NOMAD shared anchor, q-value of 4.0E-10 for donor 1, 1.2E-4 for donor 2. Scatter plots show cell-type regulation of different HLA-DRB1 alleles not explained by a null binomial sampling model p<2E-16 for donor 1, 5.6E-8 for donor 2, finite sample confidence intervals depicted in gray (Methods). Each (donor, cell-type) pair has a dominant target, per-cell fractions represented as “fraction target 1” in scatterplots, and a dominant consensus mapping to the HLA-DRB1 3’ UTR (multiway alignment); donor 1 capillary consensus contains an insertion and deletion.
D. Cell-type specific splicing of HLA-DPA1 in capillary versus macrophage cells. Anchor q-value: 7.9E-22. Detected targets are consistent with macrophages exclusively expressing the short splice isoform which excises a portion of the ORF and changes the 3’ UTR compared to the dominant splice isoform in capillary cells; splice variants found de novo by NOMAD consensuses. Binomial hypothesis test as in D for cell-type target expression depicted in scatter plots (binomial p<2.8E-14).
