Fig 6. Top multivalent minibinder candidates protect mice from SARS-CoV-2 challenge.
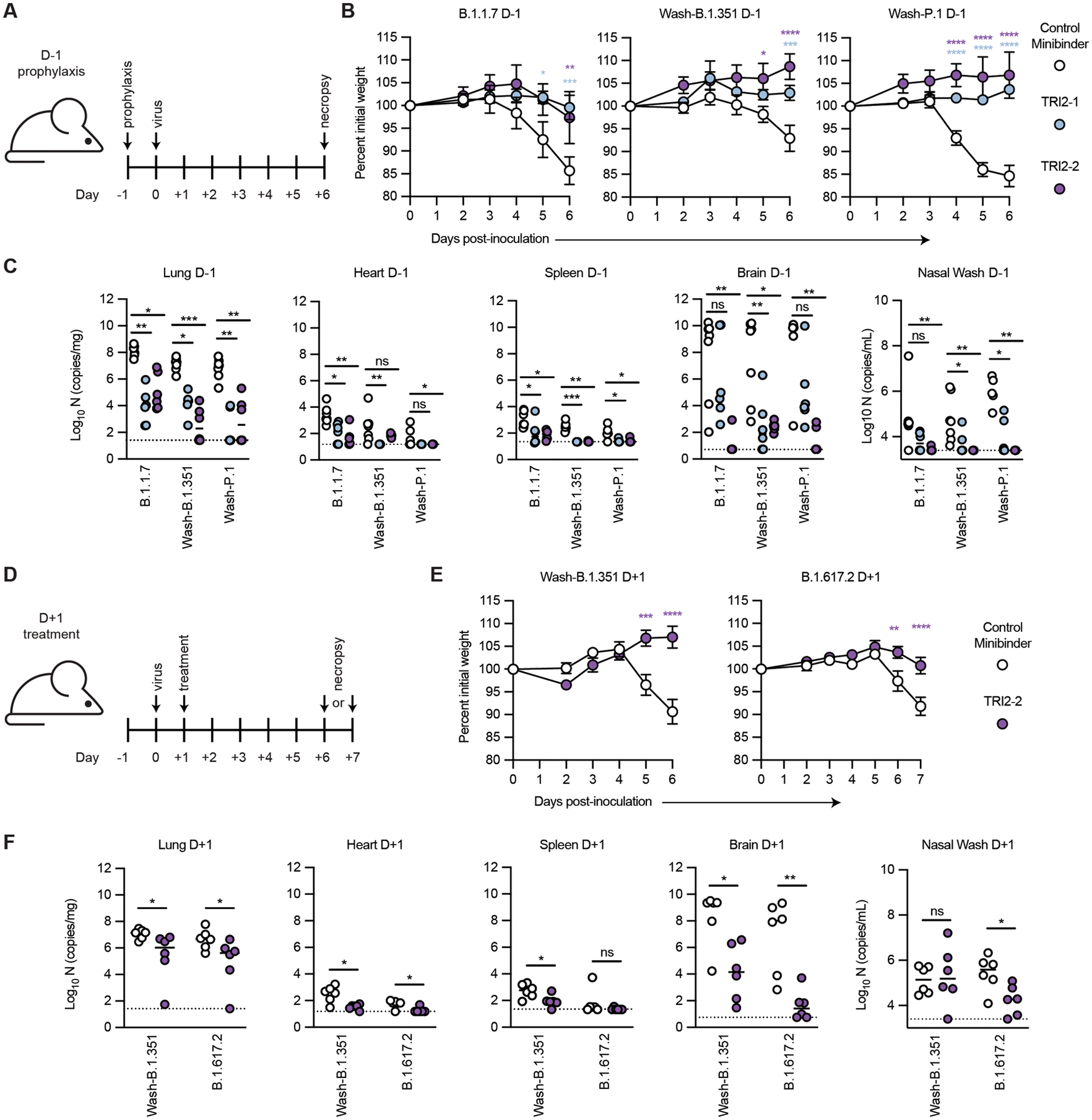
(A) K18-hACE2-transgenic mice (n = 6 from two independent experiments) were dosed with 50 μg of the indicated minibinder by intranasal (i.n.) administration (50 μl total) 24 hours prior (D-1) to infection with 103 focus forming units (FFU) of SARS-CoV-2 variants B.1.1.7, Wash-B.1.351, or Wash-P.1 i.n. on Day 0. (B) Daily weight change following inoculation was measured. Data are presented as mean ± SEM. Data were analyzed by a two-way ANOVA with Sidak’s post-test; * P < 0.05, ** P < 0.01, *** P < 0.001, **** P < 0.0001 as compared to the control minibinder. (C) At 6 days post infection (dpi), animals (n = 6 from two independent experiments) were euthanized and analyzed for SARS-CoV-2 viral RNA by RT-qPCR in the lung, heart, spleen, brain, and nasal wash. Horizontal bars indicate median; dashed lines represent the limit of detection. Data were analyzed by a Kruskal-Wallis test with Dunn’s post-hoc analysis; ns, not significant, * P < 0.05, ** P < 0.01, *** P < 0.001. (D) K18-hACE2-transgenic mice (n = 6 from two independent experiments) were dosed with 50 μg of the indicated minibinder by i.n. administration (50 μl total) 24 hours after (D+1) infection with 103 FFU of the SARS-CoV-2 Wash-B.1.351 or B.1.617.2 variant on Day 0. (E) Daily weight change following inoculation was measured. Data are presented as mean ± SEM. Data were analyzed by two-way ANOVA with Sidak’s post-test; * P < 0.05, ** P < 0.01, *** P < 0.001, **** P < 0.0001). (F) At 6 dpi (B.1.351) or 7 dpi (B.1.617.2), animals (n = 6 from two independent experiments) were euthanized and analyzed for SARS-CoV-2 viral RNA by RT-qPCR in the lung, heart, spleen, brain, and nasal wash. Horizontal bars indicate median; dashed lines represent the limit of detection. Data were analyzed by a two-tailed Mann-Whitney test; ns, not significant, * P < 0.05, ** P < 0.01.
