Fig 6.
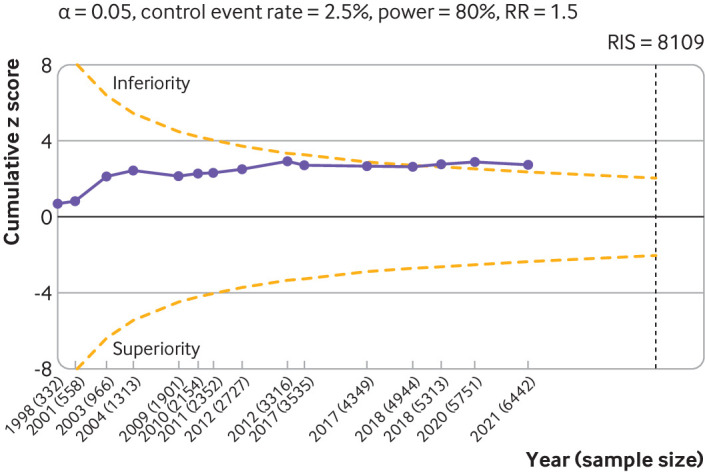
Trial sequential analysis of 15 large placebo controlled trials for serious adverse events. The analysis was based on 6462 randomised participants. Given the weak association between viscosupplementation and pain reduction in knee osteoarthritis, any increase in risk of serious adverse events caused by viscosupplementation compared with placebo can be considered a clinically important increase. Cumulative z scores are calculated under a random effects model. RIS (required information size) was calculated as the sample size that gives a trial 80% power to detect a 50% relative risk (RR) increase of serious adverse events, assuming a control event rate of 2.5% and a two sided α=0.05. O’Brien-Fleming monitoring boundaries are represented by dashed orange lines. Circles denote the z score for each additional trial. A D2 of 25% was assumed. Non-peer reviewed reports had their disclosure year defined as the earliest year in which the document was first officially created (when available within the file), year of online publication (eg, results first posted date on ClinicalTrials.gov), or the date on which the material was made available for review. Number of participants analysed (shown by year) might be smaller than number of randomised participants
