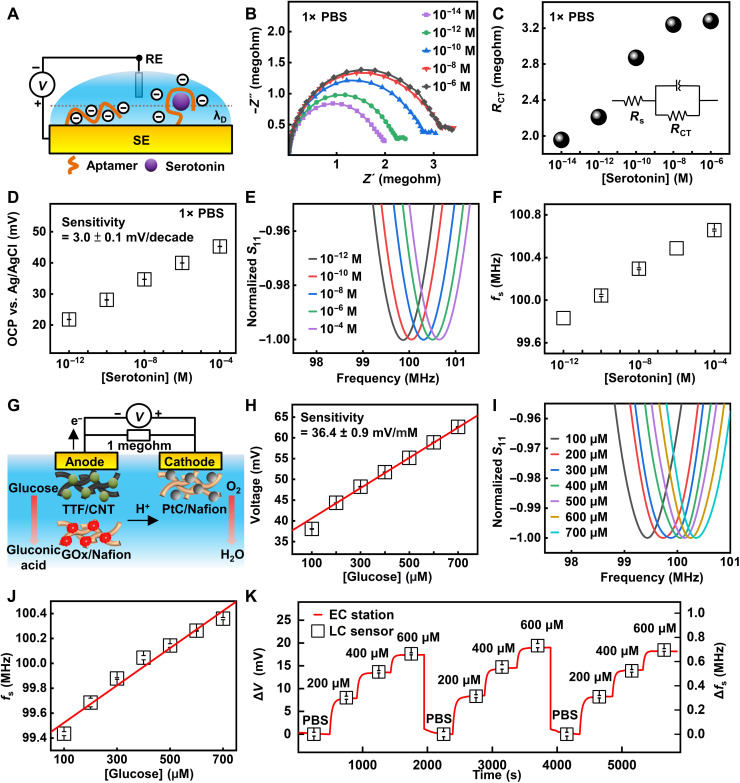
Fig. 4. Design and performance characterization of aptamer- and enzyme-functionalized sensor systems.
(A) Schematic illustration of the interaction between serotonin and an antiserotonin aptamer-functionalized Au surface. (B) EIS characterization of an aptamer-functionalized electrode in 1× PBS solutions with varying concentration of serotonin. (C) Charge transfer resistance extracted from EIS results in (B). (D) OCP (versus Ag/AgCl RE) of the sensing interface as a function of serotonin concentration in 1× PBS solution. (E) Resonance curves of a wireless sensor system integrated with antiserotonin sensing interface in response to serotonin in 1× PBS solutions. (F) fs of the integrated sensor extracted from (E). (G) Schematic illustration of the biofuel cell–inspired biochemical interface for glucose sensing. (H) Measured voltage drop across the resistor connecting the cathode and anode of the sensing interface. (I) Resonance curves of a wireless sensor system integrated with biofuel cell–inspired sensing interface in response to glucose solutions. (J) fs of the integrated sensor as a function of concentration of glucose. (K) Real-time data acquired with varying concentration of glucose measured simultaneously using an electrochemical station and a wireless sensor. The data during the three sensing cycles are collected separately with a pause between each cycle and plotted together for comparison.