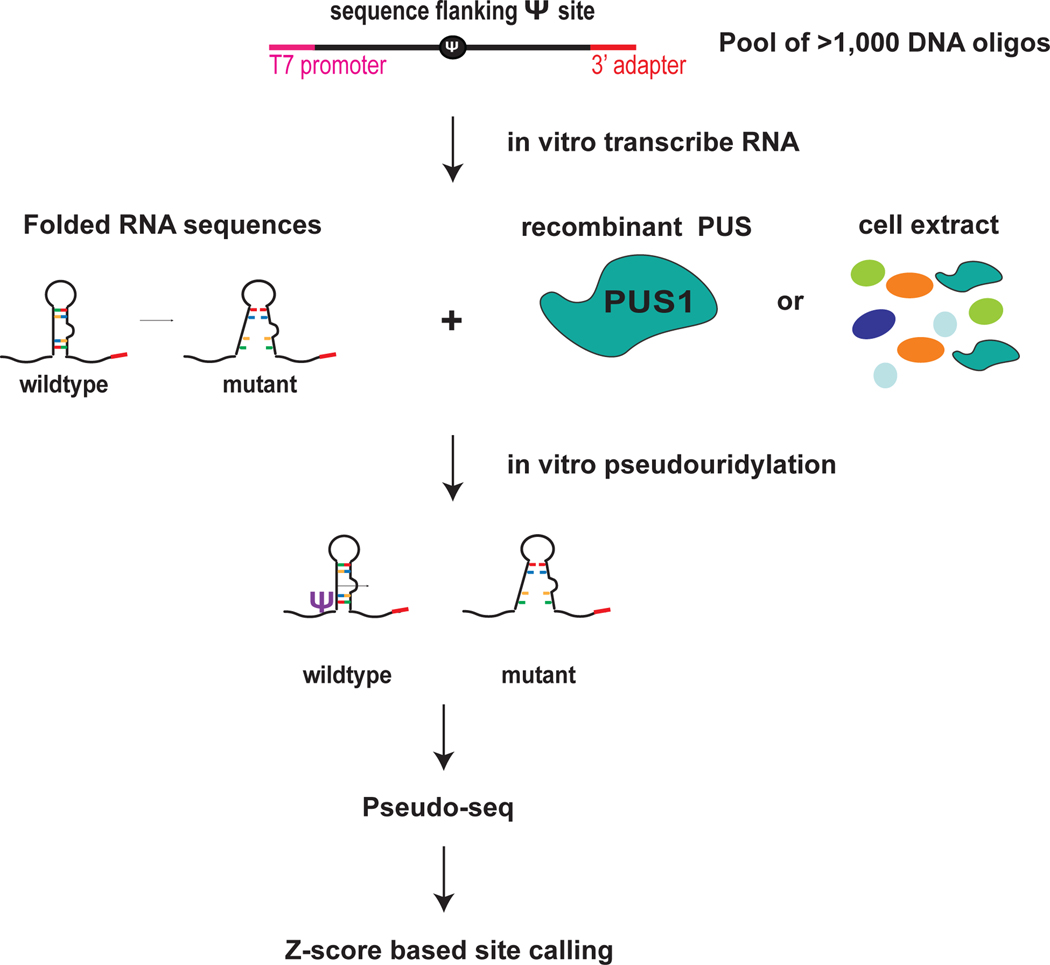
Figure 1. Highthroughput in vitro RNA pseudouridylation and sequencing.
Pool of thousands of DNA sequences that includes candidate pseduouridines and flanking sequence. Wildtype and mutant sequences can be included to interrogate the sequence and structural features that direct Ψ. The DNA oligos include a T7 promoter sequence and a 3′ adapter for PCR amplification and in vitro transcription. In vitro transcribe RNA sequeces from the DNA pool template. In vitro psedudouridylate by incubating the folded pool of RNA sequences with reocmbinant pseudouridine synthases (PUS) or cell extracts as a source of PUS. Perform Pseduo-seq to detect Ψ installed by specific PUS and to determine the effects of mutations on Ψ. Use the Z-score base approach for site calling. Figure adapted from Carlile et al. 2019 Nat Chem Bio.