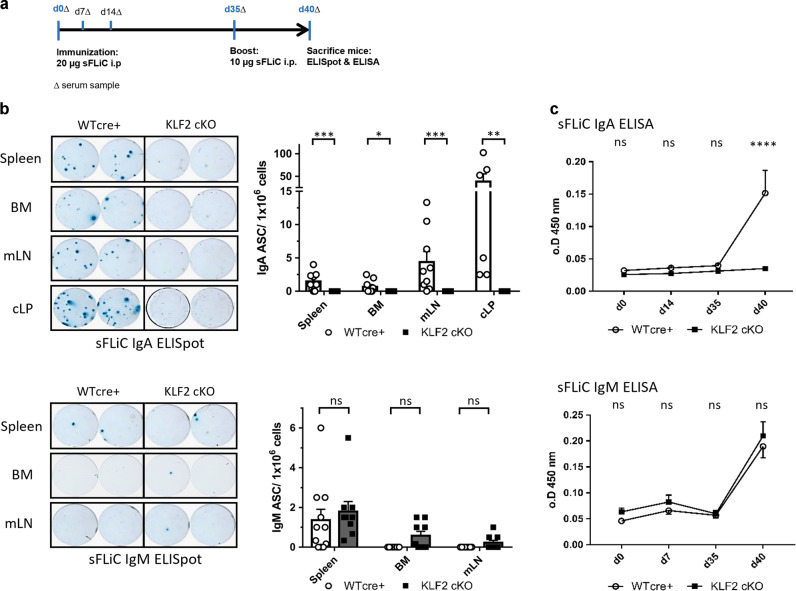
Fig. 5. KLF2-deficient animals fail to mount an antigen-specific IgA immune response to Salmonella Typhimurium antigen Flagellin (sFliC) and show impaired IgA dimerization.
a Schematic overview of the immunization workflow; serum samples (Δ) were collected on day 0 before immunization, day 7, 14 and 35 before boost immunization, as well as on day 40. b Representative ELISpots of one given cell dilution (left) and statistics (right) of the arithmetic mean with SEM of ELISpot analysis for anti-sFliC IgA (upper) and IgM (lower) antibody-secreting cells (ASC) in SP, BM, mLN and colon LP (cLP) of KLF2 cKO (gray bars, black squares) and WT cre+ control (white bars, white circles) mice. N = 3 n = 9–10 for BM, SP, mLN and n = 6 for cLP, removal of definitive outliers by ROUT (Q = 0.1%) test, statistics was performed applying a Mann–Whitney U test; c Arithmetic means with SEM of relative optical densities (o.D.) of sFliC-specific serum IgA (upper) and IgM (lower) at indicated time points after immunization of KLF2 cKO (black squares) and WT cre+ control (white circles) mice; n = 5, statistical analyses were performed for time point and genotype comparison by two-way ANOVA with Sidak’s correction for multiple comparisons. PB plasmablast, PC plasma cell, BM bone marrow, mLN mesenteric lymph nodes, cLP colon lamina propria, sFliC soluble recombinant Flagellin antigen, ASC antibody-secreting cells, o.D. optical density, ns non-significant; *p < 0.05; ***p < 0.005; ****p < 0.001.