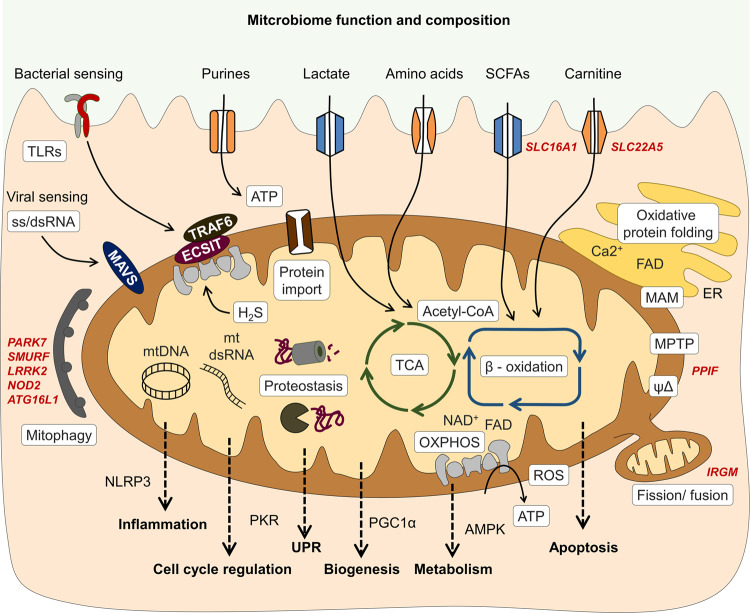
Fig. 3. Intestinal epithelial cell mitochondria serve as metabolic signaling platform translating microbiome-derived signals into mucosal responses.
Intestinal epithelial cells (IECs) sense the microbial environment via pattern recognition receptors including toll-like receptors (TLR) and take up diet and microbiota-derived metabolites. Activation of TLR signaling can impact the electron transport chain (ETC) and oxidative phosphorylation (OXPHOS) via TNF receptor associated factor (TRAF) 6 and ECSIT (Evolutionarily conserved signaling intermediate in Toll pathway), altering production of reactive oxygen species (ROS). Viral sensing involves mitochondrial antiviral-signaling protein (MAVS) and initiates inflammatory responses i.e., activating NFκB pathway. Microbiota-derived metabolites feed the tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle and mitochondrial beta oxidation or can enhance cellular energetics through salvage pathways (purines). Hydrogen sulfide (H2S) produced by bacteria can as electron donor for the ETC, but at high concentrations, inhibit Complex IV activity and other mitochondrial proteins. Mitochondria are embedded in an organelle network, in particular, an exchange of calcium, FAD, and ATP with the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) occurs at mitochondria-associated membranes (MAM) and is important for ER oxidative protein folding. Proteostasis, depending on protein import, chaperone activity, and proteases, is crucial to sustain mitochondrial functions, and disturbances of mitochondrial proteostasis are signaled by the mitochondrial unfolded protein response (UPRmt). Release of mitochondrial DNA and double-stranded (ds) mitochondrial RNA184 under stress conditions promotes inflammatory signaling and regulates cell cycle progression. Fission and fusion events as well as mitophagy are critical regulators of mitochondrial homeostasis and prevent accumulation of dysfunctional mitochondria and excess ROS production. Thus, mitochondria integrate environmental signals into metabolism, downstream employing various signaling pathways to contribute to cell fate decisions and determine cellular phenotypes. Gene names of known IBD risk variants involved in mitochondrial functions are given in dark red. AMPK AMP-activated protein kinase, NLRP3 NLR family pyrin domain containing 3, PGC1α Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma coactivator 1-alpha, PKR double-stranded RNA-activated protein kinase, SCFAs short chain fatty acids.