Fig. 3. Molecular details of stalk and arches protein structures and interactions, and structure validation by co-evolution analysis.
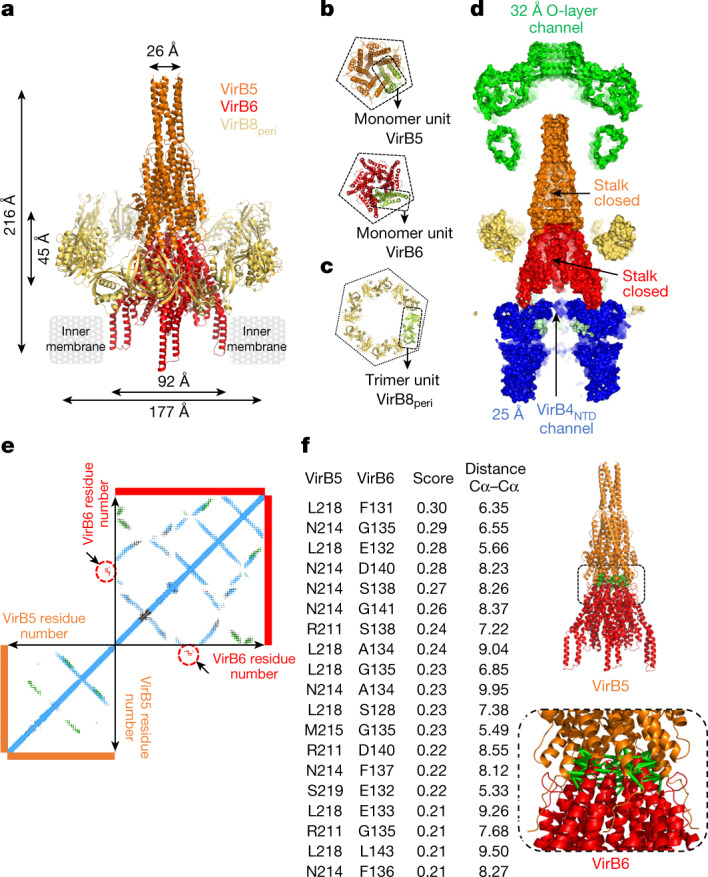
a, Overall structure of the stalk and arches. Stalk and arches proteins are shown in ribbon coloured orange (VirB5), red (VirB6) and yellow (VirB8peri). Proteins constituting the complexes and the dimensions of the two sub-complexes—stalk and arches—are indicated. b, Symmetry arrangements of VirB5 and VirB6. All proteins are shown in ribbon representation, colour-coded as in a, except one monomer in each box is shown in green. Top, bottom view of the VirB5 pentamer. Bottom, bottom view of the VirB6 pentamer. The dashed line in both illustrates the pentameric nature of each structure. c, Top view of the arches, showing the symmetry arrangement of VirB8peri. All proteins are shown in ribbon representation. The arches are made of six trimeric units of VirB8peri, one of which is shown in pale green and outlined; the rest are colour-coded as in a. The hexagon surrounding the hexamer of trimer highlights the six-fold symmetrical arrangement of this part of the structure. d, Cross-section of the T4SS surface. The channels are shown with dimensions of interest. The VirB4outside subunits are not shown. e, Co-evolution at the interface of VirB5 and VirB6. Results of computational analysis. Each dot represents a pair of co-evolving residues with TrRosetta score ≥0.21. Dots are coloured blue (intra-protein co-evolution pairs), green (homo-oligomeric co-evolution pairs) or red surrounded by red circles and located by arrows (hetero-oligomeric co-evolution pairs). f, Co-evolution at the interface of VirB5 and VirB6. Left, list of hetero-oligomeric co-evolution pairs with TrRosetta scores above the threshold of 70% (Methods and main text) and Cα–Cα distances in angstrom in the structure reported here. Numbering is that of the R388 proteins. Full list in Supplementary Table 4. Right, mapping of co-evolution pairs listed in the table onto the VirB5–VirB6 stalk sub-complex structure. Pairs of residues across the interface are linked by green bars.
