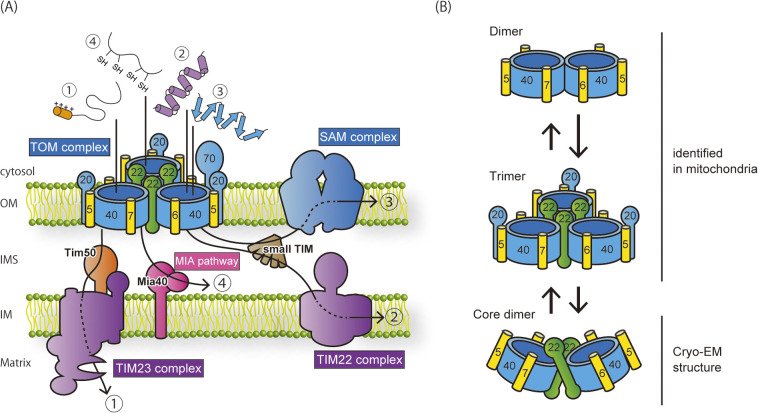
Figure 1 .
Import pathways of mitochondrial proteins. (A) Four major import pathways and translocators are shown. Upon translocation into the IMS through the TOM complex in the OM, the import pathway is branched to four different pathways. Pathway 1: presequence-containing preproteins are inserted into the IM or transported to the matrix through the TIM23 complex. Pathway 2: polytopic inner-membrane proteins, such as carrier-family proteins, are transferred to the IMS chaperones, small TIM proteins, and inserted into the IM by the TIM22 complex. Pathway 3: β-barrel proteins are transferred to the small TIM proteins and inserted into the OM by the SAM complex. Pathway 4: small soluble IMS proteins are transferred to Mia40 and undergo oxidative folding in the IMS. This schematic diagram is modified from Ref. 4. (B) Different assembly forms of the TOM complex. In intact mitochondria, the TOM complex exists in a dynamic exchange between a major form of the trimer and a minor form of the dimer lacking Tom22 and Tom20. The purified TOM complex in detergent micelles is a mixture of the trimer and the dimer, which contains Tom22 but not Tom20, named the core dimer.