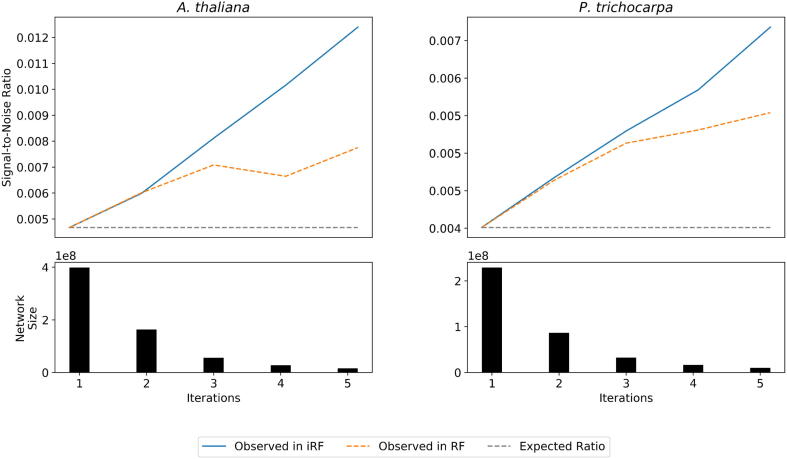
Fig. 3.
In this figure, the blue line depicts the truly observed signal-to-noise ratio for each network as the number of iterations in iRF increases. As the iterations increase, a number of edges are dropped from consideration due to their importance scores equaling zero. To confirm that the improvement in signal-to-noise ratio is not due to simply thresholding the networks, the RF network is thresholded to match the network size of the iRF network at each iteration and is depicted as the orange dashed line. For both A. thaliana and P. trichocarpa, the observed signal-to-noise ratio in iRF is greater than both what is expected from random and if the RF network is simply thresholded. This shows that the unsupervised thresholding from iRF provides an improvement over a simple manual thresholding.