Table 1.
Quality of evidence for the outcomes.
| SC semaglutide and oral semaglutide compared to placebo or GLP-1 RA comparator for HbA1c, body weight, and AEs | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Patient or population: HbA1c, body weight, and AEs Setting: Intervention: SC semaglutide and oral semaglutide Comparison: Placebo or GLP-1 RA comparator | |||||
| Outcomes | No. of participants (studies) Follow up |
Certainty of evidence (GRADE) | Relative effect (95% CI) | Anticipated absolute effects |
|
| Risk with placebo or GLP-1 RA comparator | Risk difference with SC semaglutide and oral semaglutide | ||||
| Semaglutide vs placebo - semaglutide 1.0 mg vs placebo | 825 (3 RCTs) | 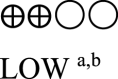 |
– | Mean semaglutide vs placebo - semaglutide 1.0 mg vs placebo was 8.07% | MD 1.55% lower (1.75 lower to 1.36 lower) |
| Semaglutide vs placebo - semaglutide 1.0 mg vs comparator | 1985 (3 RCTs) | 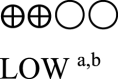 |
– | Mean semaglutide vs placebo - semaglutide 1.0 mg vs GLP-1 RA comparator was 7.13% | MD 0.58% lower (0.75 lower to 0.41 lower) |
| Oral semaglutide vs placebo - oral semaglutide 14 mg | 1566 (5 RCTs) | 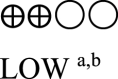 |
– | Mean oral semaglutide vs placebo - oral semaglutide 14 mg was 8.06% | MD 1.29% lower (1.47 lower to 1.11 lower) |
| Oral semaglutide vs placebo - oral semaglutide 14 mg vs GLP-1 comparator | 860 (3 RCTs) | 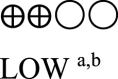 |
– | Mean oral semaglutide vs placebo - oral semaglutide 14 mg vs GLP-1 RA comparator was 7.03% | MD 0.31% lower (0.44 lower to 0.17 lower) |
| Body weight semaglutide vs placebo - semaglutide 1.0 mg vs placebo | 824 (3 RCTs) | 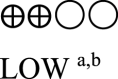 |
– | Mean body weight semaglutide vs placebo - semaglutide 1.0 mg vs placebo was 90.57 kg | MD 4.16 kg lower (5.05 lower to 3.26 lower) |
| Body weight semaglutide vs placebo - semaglutide 1.0 mg vs GLP-1 RA comparator | 1985 (3 RCTs) |  |
– | Mean body weight semaglutide vs placebo - semaglutide 1.0 mg vs GLP-1 RA comparator was 93.7 kg | MD 3.72 kg lower (4.17 lower to 3.28 lower) |
| Body weight oral semaglutide vs placebo or GLP-1 RA comparator - semaglutide 14 mg vs placebo | 1793 (5 RCTs) | 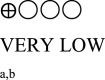 |
– | Mean body weight oral semaglutide vs placebo or GLP-1 RA comparator - semaglutide 14 mg vs placebo was 85.22 kg | MD 3.18 kg lower (4.12 lower to 2.24 lower) |
| Body weight oral semaglutide vs placebo or GLP-1 RA comparator - semaglutide 14 mg vs GLP-1 RA comparator | 860 (3 RCTs) | 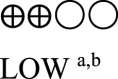 |
– | Mean body weight oral semaglutide vs placebo or GLP-1 RA comparator - semaglutide 14 mg vs GLP-1 RA comparator was 78.38 kg | MD 2.42 kg lower (3.18 lower to 1.66 lower) |
| AEs, semaglutide vs placebo or GLP-1 RA comparator - semaglutide vs placebo | 1084 (3 RCTs) |  |
RR 1.14 (1.03–1.26) | 574 per 1,000 | 80 more per 1,000 (17 more to 149 more) |
| AEs, semaglutide vs placebo or GLP-1 RA comparator - semaglutide vs GLP-1 RA comparator | 2584 (3 RCTs) |  |
RR 1.01 (0.96–1.06) | 702 per 1,000 | 7 more per 1,000 (28 fewer to 42 more) |
| AEs oral semaglutide vs placebo or GLP-1 RA comparator - oral semaglutide vs placebo | 1971 (5 RCTs) | 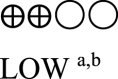 |
RR 1.07 (0.99–1.16) | 674 per 1,000 | 47 more per 1,000 (7 fewer to 108 more) |
| AEs oral semaglutide vs placebo or GLP-1 RA comparator - oral semaglutide vs GLP-1 RA comparator | 1042 (3 RCTs) |  |
RR 1.06 (0.99–1.14) | 744 per 1,000 | 45 more per 1,000 (7 fewer to 104 more) |
| *The risk in the intervention group (and its 95% confidence interval [95% CI]) is based on the assumed risk in the comparison group and the relative effect of the intervention (and its 95% CI). CI: confidence interval; MD: mean difference; RR: risk ratio; SC: subcutaneous, AE: adverse events. | |||||
|
GRADE Working Group grades of evidence High certainty: We are very confident that the true effect lies close to that of the estimated effect. Moderate certainty: We are moderately confident in the effect estimate; the true effect is likely to be close to the estimated effect, but there is a possibility that it is substantially different. Low certainty: Our confidence in the effect estimate is limited; the true effect may be substantially different from the estimated effect. Very low certainty: We have very little confidence in the effect estimate; the true effect is likely to be substantially different from the estimated effect. | |||||
Explanations.
a. The quality was downgraded because some studies were not blinded.
b. The quality was downgraded because of high heterogeneity across studies.
