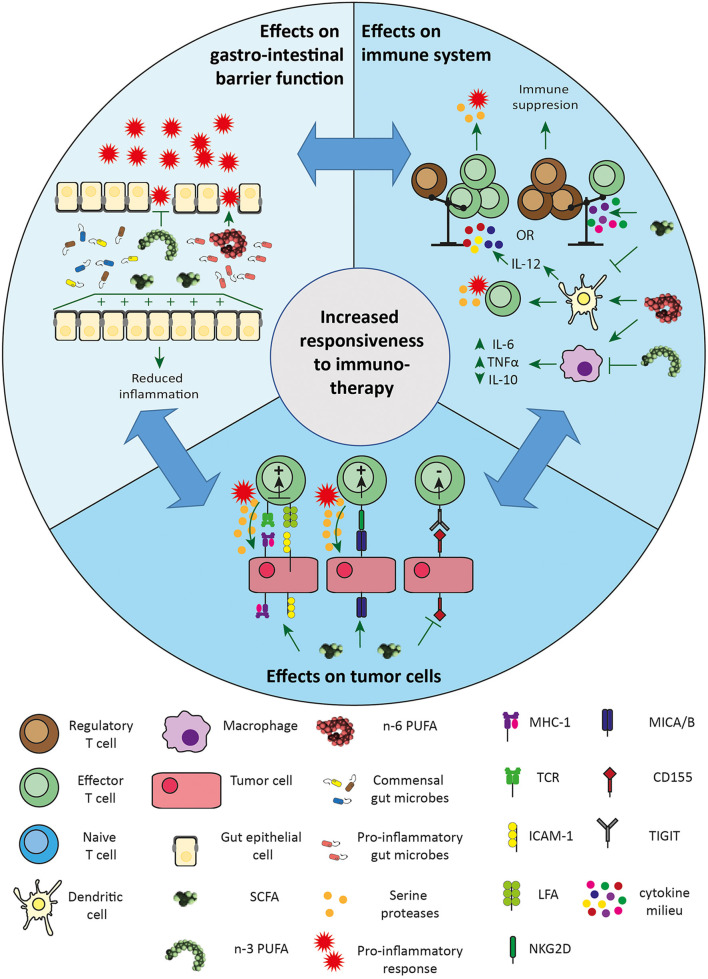
Figure 1.
Proposed mechanisms through which SCFAs and PUFAs enhance immunotherapy efficacy. Effects on gastric barrier: SCFAs can improve gut barrier function and have, as well as n-3 PUFAs, anti-inflammatory effects. Diets rich in n-3 PUFAs have a beneficial effect on the gut microbiome. Both have beneficial effects on gastro-intestinal functioning, thereby reducing immune-mediated toxicity and may enhance to immunotherapy outcome, as the need of cessation of treatment is lower. Diets rich in n-6 PUFAs lead to dysbiosis accompanied with pro-inflammatory effects. Effects on immune system: SCFAs promote T cell differentiation in both effector T cells and regulatory T cells, depending on the cytokine milieu. SCFAs also inhibit IL-12 secretion from dendritic cells modulating effector T cell activation. Contrary, n-6 PUFAs enhance dendritic cell capacity to stimulate cytotoxic T cell activity, directly reducing tumor growth. n-6 PUFAs' pro-inflammatory effects occur mainly via stimulation of macrophages contributing to chronic low-grade inflammation. In contrast, n-3 PUFAs suppress inflammation via reducing IL-6 and TNFα and increasing IL-10 production. Effects on tumor cells: SCFAs enhance the expression of MHC-1 and ICAM-1 on tumor cells, making them more sensitive to cytotoxic lymphocytes-mediated killing. SCFAs also induce the expression of MICA/B on tumor cells, making them a target for effector T cells via the NKG2D receptor. SCFAs reduce the expression of CD155 on tumor cells, inhibiting the interaction with TIGIT expressed on effector CD8+ T cells. ICAM-1, intercellular adhesion molecule 1; IL-6, interleukin 6; IL-10, interleukin 10; IL-12, interleukin 12; LFA, lymphocyte function-associated antigen 1; MHC-1, major histocompatibility complex 1; MICA/B, MHC class I polypeptide-related sequence A/B; NKG2D, natural killer group 2D; n-3 PUFAs, omega 3 polyunsaturated fatty acids; n-6 PUFAs, omega 6 polyunsaturated fatty acids; SCFAs, short chain fatty acids; TCR, T cell receptor; TIGIT, T cell immunoreceptor with Ig and ITIM domains; TNFα, tumor necrosis factor α.