Table 1.
Development of catalytic reaction conditions.
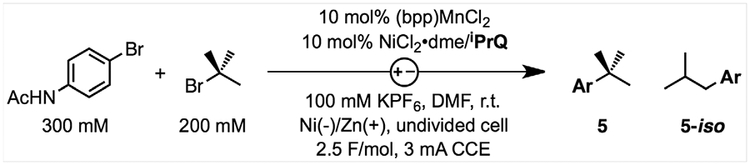
| ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Entry | Deviation from standard conditions | %conv ArBr | %yield 5 | %yield 5-iso |
| 1 | Standard conditions | 86 | 75 | 0 |
| 2 | (bpp)NiCl2 instead of [(bpp)MnCl2 + NiCl2•dme] | 92 | 83 | 8 |
| 3 | (bpp)Co(OAc)2 instead of (bpp)MnCl2 | 72 | 35 | 6 |
| 4 | (bpp)FeBr2 instead of (bpp)MnCl2 | 74 | 29 | 11 |
| 5 | Constant current: 6 mA | 82 | 49 | 1 |
| 6 | Constant current: 1.5 mA | 62 | 45 | 0 |
| 7 | Constant voltage: Ecell = 0.4 V | 81 | 47 | 0 |
| 8 | Constant voltage: Ecell = 0.6 V | 89 | 53 | 1 |
| 9 | No NiCl2•dme | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 10 | No (bp)MnCl2 | 7 | 0 | 0 |
| 11 | No iPrQ ligand | 6 | 5 | 1 |
| 12 | Zn0 anode, no e-chem | 24 | 17 | 1 |
| 13 | Zn0 powder (3 equiv), no e-chem | 74 | 60 | 5 |
| 14 | 5 mol% iPrQ | 78 | 43 | 1 |
| 15 | 15 mol% iPrQ | 84 | 68 | 0 |
| 16 | 200 mM ArBr and 200 mM tBuBr | 100 | 57 | 0 |
Calibrated GC yields against an internal standard are reported. CCE, constant current electrolysis.
