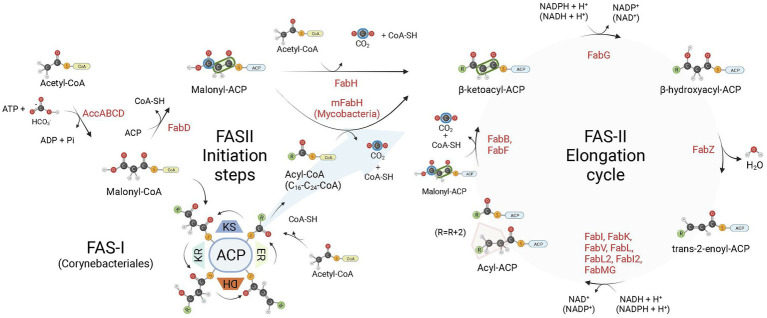
Figure 1.
Bacterial fatty acid biosynthesis. There are two types of fatty acid (FA) biosynthesis in nature, FAS-I and FAS-II. In both pathways, fatty acid chains are elongated through iterative cycles in which two-carbon units are added after each cycle. Most bacteria rely exclusively on FAS-II pathway for FA synthesis, some members of the Corynebacteriales order, on the other hand, rely exclusively on FAS-I, while mycobacteria and most corynebacteria (mycolic acid-producing organisms) possess FAS-I and FAS-II pathways. In both systems, there are four sequential steps in each elongation cycle: (1) condensation of acyl and malonyl groups, (2) β-ketoacyl-ACP reduction, (3) β-hydroxyacyl-ACP dehydration, and (4) trans-2-enoyl-ACP reduction, leading to an extended acyl chain containing 2 additional carbon units. In FAS-I, a single megasynthase performs the four sequential steps of chain elongation, while in FAS-II different enzyme components perform each step. The first committed step in FA synthesis is the carboxylation of acetyl-CoA by the enzyme acetyl-CoA carboxylase (AccABCD), leading to the production of malonyl-CoA from acetyl-CoA. During the elongation steps of preformed acyl chains, malonyl-CoA units are the malonyl donor groups in the FAS-I condensation step (ketoacyl synthase, KS), while in FAS-II it is first converted to malonyl-ACP by FabD, which is then used by FabB (or FabF) as the malonyl donor group in the condensation step of FAS-II elongation. In FAS-I, chain initiation requires the condensation of acetyl-CoA and malonyl-CoA by the KS activity of the megasynthase. For bacteria relying exclusively on FAS-II for FA synthesis, the initiation step requires the production of acetoacetyl-ACP (a β-ketoacyl-ACP species) from the condensation of malonyl-ACP and acetyl-CoA performed by FabH. When both FAS-I and FAS-II systems are available, as in mycobacteria, preformed acyl-CoA chains containing from C16-C24 carbon units derived from the FAS-I system are shuttled into FAS-II by an initial condensation step with malonyl-ACP catalyzed by mFabH. Bacterial enoyl-ACP reductases (ENRs) catalyze the last step of trans-2-enoyl-ACP reduction of the FAS-II cycle. ACP, Acyl Carrier Protein; KR, β-ketoacyl-ACP reductase activity; DH, β-hydroxyacyl-ACP dehydrogenase activity; ER, trans-2-enoyl-ACP reductase activity. Created with BioRender.com.