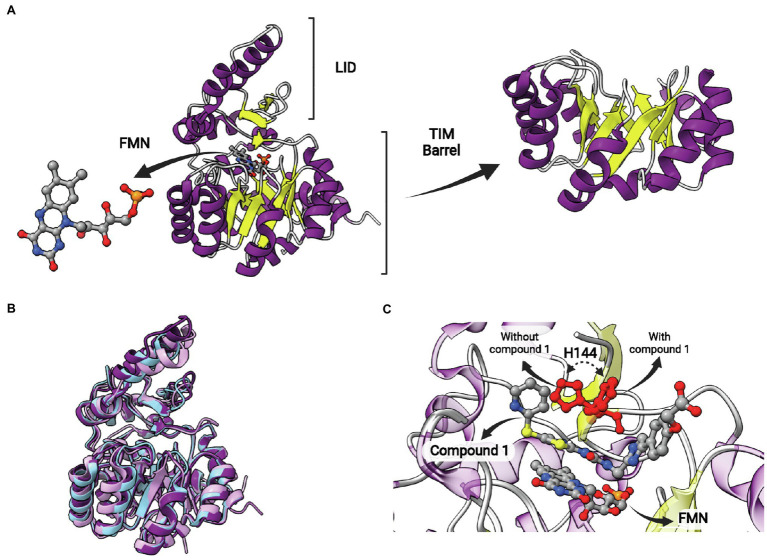
Figure 12.
FabK structure. (A) Structure of Streptococcus pneumoniae FabK (SpFabK, PDB: 2Z6I). The LID and the TIM barrel fold are indicated. The latter, together with a bound flavin mononucleotide (FMN) cofactor, are represented in more detail. (B) Superposition of Porphyromonas gingivalis FabK (PgFabK, PDB: 4IQL, represented in pink) with Thermotoga maritima FabK (TmFabK, PDB: 5GVH, represented in cyan) and S. pneumoniae FabK (SpFabK, PDB: 2Z6I, represented in purple). (C) Superposition of SpFabK bound to FMN cofactor (PDB: 2Z6I) with the ternary structure of SpFabK bound to FMN and a phenylimidazole derivative inhibitor (compound 1; PDB: 2Z6J). The orientation of a putative catalytic histidine residue (H144) rotates upon inhibitor binding. The superposition of structures was performed using the Matchmaker tool from UCSF ChimeraX. Created with UCSF ChimeraX (Pettersen et al., 2021) and BioRender.com.