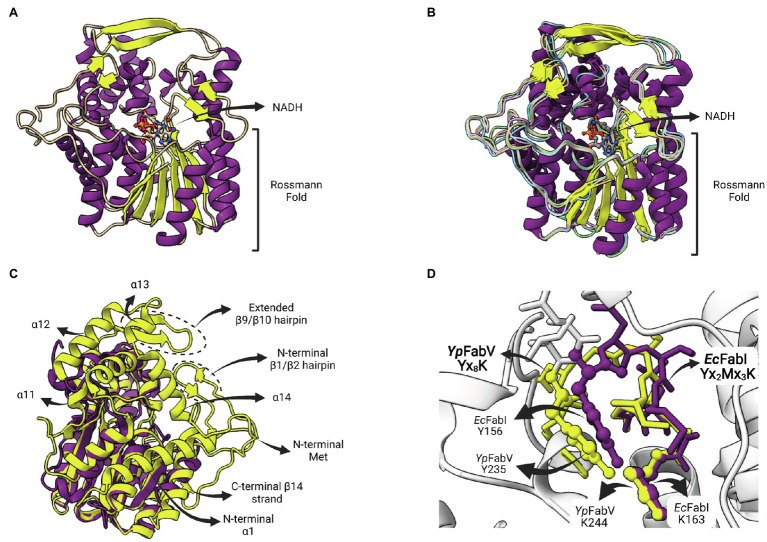
Figure 9.
FabV structure. (A) Structure of Yersinia pestis FabV (YpFabV—PDB: 3ZU3). The bound cofactor NADH and the eight-stranded Rossmann fold shared by FabVs are indicated. (B) Superposition of available FabV structures: Y. pestis YpFabV (PDB: 3ZU3), Xanthomonas oryzae XoFabV (PDB: 3S8M), Burkholderia pseudomallei BpFabV (PDB:4BKO) and Vibrio fischeri VfFabV (PDB:5XI0). (C) Superposition of YpFabV (PDB: 3ZU3) with EcFabI (PDB: 1C14). Structure of EcFabI is depicted in purple while structure of YpFabV is in yellow. Some structural elements of FabV ENRs not found in FabIs are indicated. (D) Structural comparison between the FabV extended active site signature motif Yx8K (from YpFabV—PDB: 3ZU3) and the Yx6K (Yx2Mx3K) motif of FabIs (from EcFabI—PDB: 1C14) reveals that the position of the catalytic lysine is almost identical, while the position of the catalytic tyrosine is very similar, in particular its hydroxyl oxygen atom. The superposition of structures was performed using the Matchmaker tool from UCSF ChimeraX. Created with UCSF ChimeraX (Pettersen et al., 2021) and BioRender.com.