Figure 3. Role of fibrillin-1 in the SMCs.
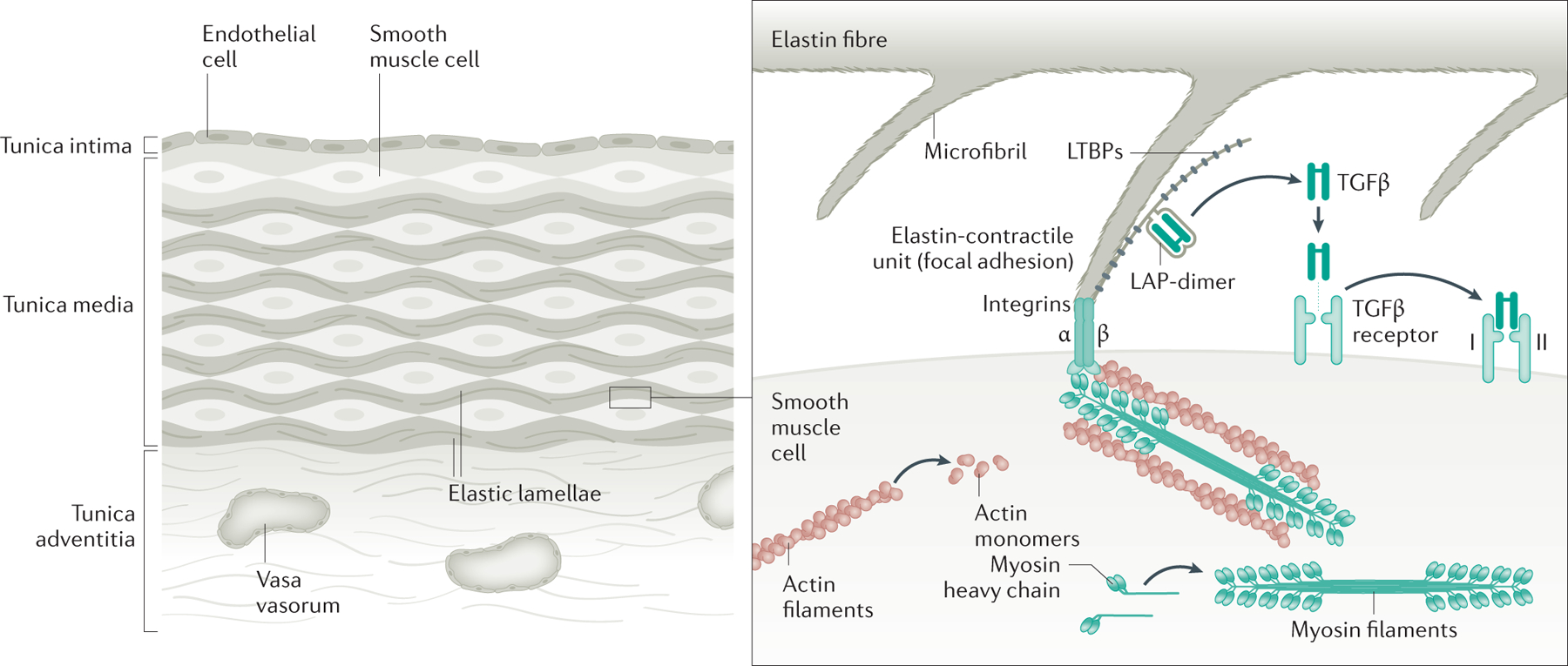
The human aorta is composed of over 50 layers of elastic lamellae and SMCs (note that for simplicity only a few layers are shown). Elastin fibers have oblique extensions that have microfibrils at the tips, which connect to focal adhesions on the SMC cell surface, and then to SMC contractile units; these structures are called elastin-contractile units. Fibrillin-1 is the major protein in the connecting microfibrils. Genes that are altered to predispose to heritable thoracic aortic disease disrupt major proteins in the elastin-contractile unit. Research has focused on the role of excessive TGF-β and angiotensin II signalling as drivers of thoracic aortic disease. More recent research has indicated that loss of TGF-β signalling is a primary driver of thoracic aortic disease, but increased signaling may have a role in late stages of the disease process.
