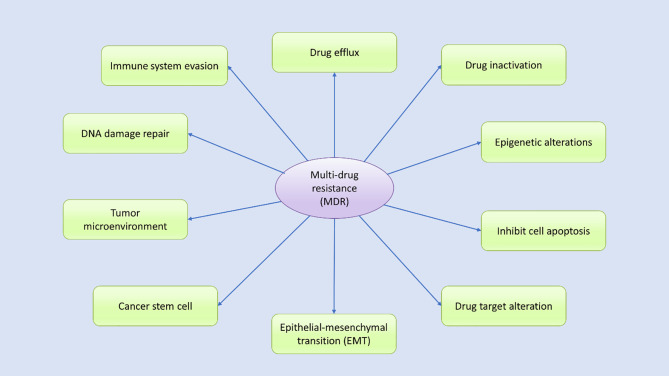
Figure 2.
Various potential mechanisms contribute to multidrug resistance. Many internal and external factors have been associated with the development of multidrug resistance in human cancer cells through either direct or indirect effects. Drug efflux, changes in cellular drug levels, drug inactivation, altered epigenetic states, epithelial–mesenchymal transition (EMT), the tumor microenvironment, DNA damage repair, cancer stem cell propagation, and immune system evasion are well-studied mechanisms thought to contribute to MDR through various signal transduction pathways, either independently or in combination.