Figure 7.
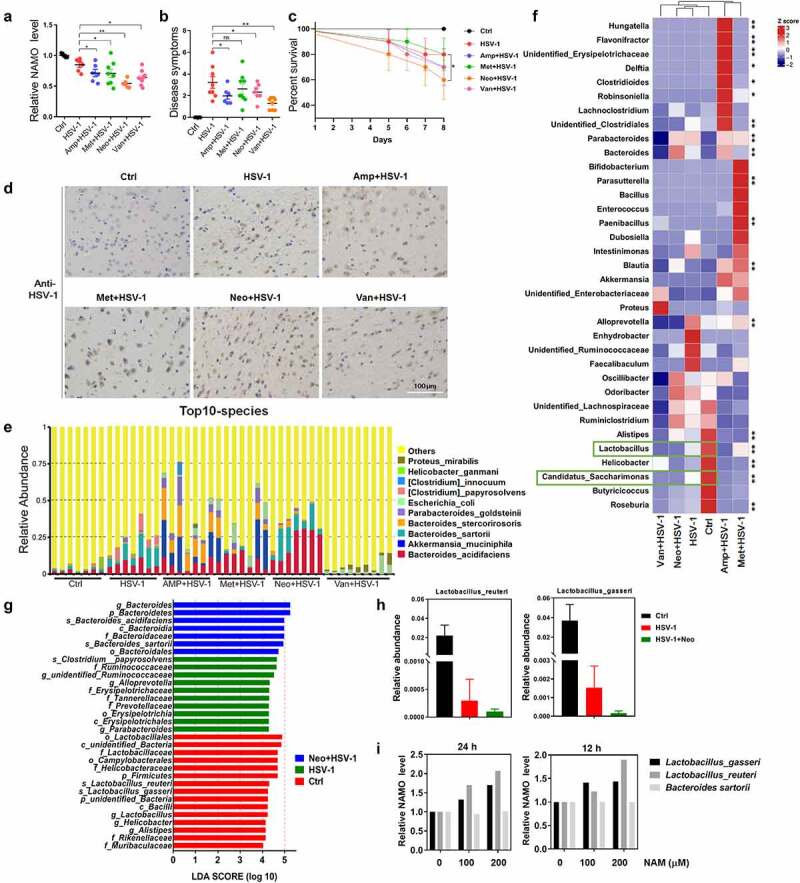
Nicotinamide N-oxide is generated by neomycin-sensitive bacteria. (a) Serum NAMO levels of HSV-1-infected mice pretreated with vancomycin (van), ampicillin (amp), neomycin (neo) or metronidazole (met), respectively. Each symbol represents data from one mouse. n = 6–10 mice per group. Data are mean ± SD. *p < .05, **p < .01, or ***p < .001 versus HSV-1 group by t test. (b-d) Neomycin-pretreated mice exhibited aggregated HSE symptoms related to neurological disease score (b), shortened survival rate compared with normal or ABX-treated mice (c), and enhanced virus production in OB as revealed by IHC assay (d). n = 6–10 mice per group. *p < .05, **p < .01, or ***p < .001 versus HSV-1 group by t test. Scale bar, 100 μm. (e) Top 10 microbes at the species level in fecal samples from Ctrl, HSV-1 and HSV-1 + antibiotic mice, respectively. n = 6–10 mice per group. (f) Metastats analysis of the correlation between the altered bacteria in genus level. Colors on the heatmap indicate the relative abundance. Red indicates bacteria that are upregulated, and blue represents downregulated. Green squares indicate bacterial genus whose levels were significantly downregulated by HSV-1 but further reduced by neomycin. **p < .01, ***p < .001 versus HSV-1 group. (g) LEfSe analysis showed the taxa most differentially abundant among ctrl, HSV-1 and HSV-1+ Neo groups. Only taxa meeting an LDA significant threshold value of ≥ 2.0 are shown. (h) Relative abundance of bacterial species Lactobacillus_gasseri and Lactobacillus_reuteri in feces samples from Ctrl, HSV-1 and HSV-1+ Neo group. (i) NAMO levels in bacterial supernatant. Bacterial cultures of L. gasseri, L. reuteri and B. sartorii were incubated with NAM for 12 h or 24 h at 37°C. NAMO was then detected by UPLC–MS/MS. Data are mean ± SD (n = 5). Significance as *p < .05, **p < .01, ***p < .001 by t test.
