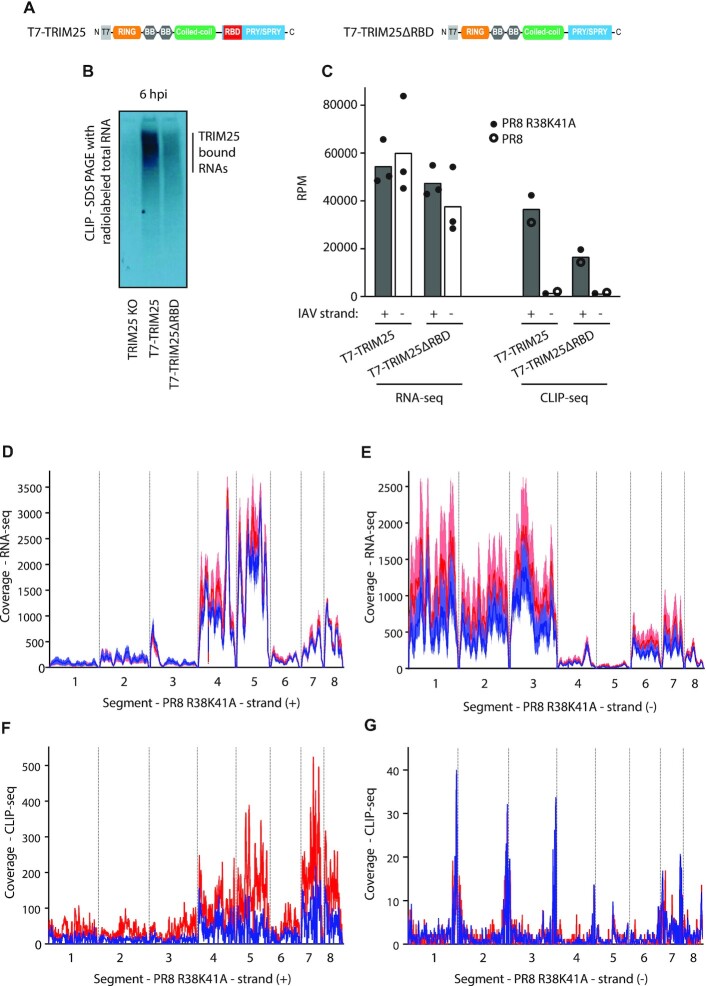
Figure 2.
TRIM25 preferentially binds positive-sense IAV RNAs. (A) Domain architecture of wild-type TRIM25 and TRIM25ΔRBD tagged with T7. (B) T7-TRIM25 binds efficiently to RNA, while TRIM25ΔRBD RNA-binding is somewhat compromised, as seen on the SDS PAGE with 5′-end labeled, total RNA crosslinked and immunoprecipitated with anti-T7 Ab, 6 hpi (hours post infection) with the PR8 R38K41A IAV (MOI = 5). (C) RNA-seq analyses of HEK293 cells 6 hpi with the PR8 R38K41A IAV (MOI = 5) (filled circles) show comparable levels of (+) and (–) IAV strands, whereas CLIP-seq analyses of both T7-TRIM25 and T7-TRIM25ΔRBD infected with PR8 (empty circles) or PR8 R38K41A (filled circles) display preference for binding to (+) IAV strand RNAs. Bars represent geometric mean number of reads per million (RPM). (D, E) Coverage depth (reads) for the PR8 R38K41A IAV ((+) panel D, and (–) panel E) detected at 6 hpi with RNA-seq in T7-TRIM25 (red line) and T7-TRIM25ΔRBD cells (blue line). Line represents mean values (n = 3). Shaded area represents ranges. (F, G) Coverage depth (reads) for the PR8 R38K41A IAV ((+) panel F, and (–) panel G) detected 6 hpi with the CLIP-seq in T7-TRIM25 (red line) and T7-TRIM25ΔRBD cells (blue line). For analysis and presentation all segments were joined together. Coverage depth was adjusted per million of reads after quality trimming.