Figure 2.
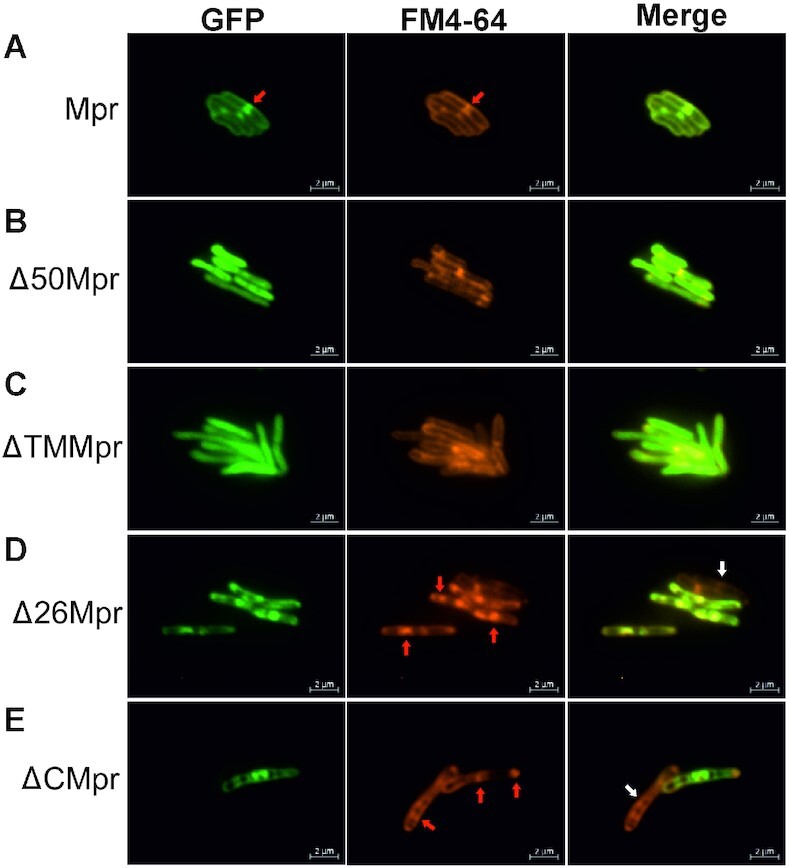
Fluorescent microscopy images of Mpr and its truncations. Respective gene/truncations are cloned with N-terminal GFP tag and expressed in MsmWT. (A) Mpr is observed to colocalize with FM4-64, suggesting membrane localization in vivo. (B) Deletion of first 50 amino acids (Δ50Mpr) renders protein unable to anchor to membrane. (C) loss of TM region (ΔTMMpr) restricts the protein in cytosol. (D) Deletion of first 26 amino acids (Δ26Mpr) does not affect localization of Mpr to the membrane. (E) N-ter region after deletion of C-terminal region (ΔCMpr) still localizes to the membrane. The truncations containing intact TM region show toxicity and cause aggregation in membrane affecting membrane integrity (shown with red arrow). Due to toxicity caused by protein expression, cells most likely lose plasmid and hence, no GFP expression is observed (shown with white arrow). Localization of protein is shown under GFP column. FM4-64 (specific for membrane localization) is used as a reference. Merge of GFP and FM4-64 channel shows relative localization of the target protein. Scale is shown at the bottom right of each image.
