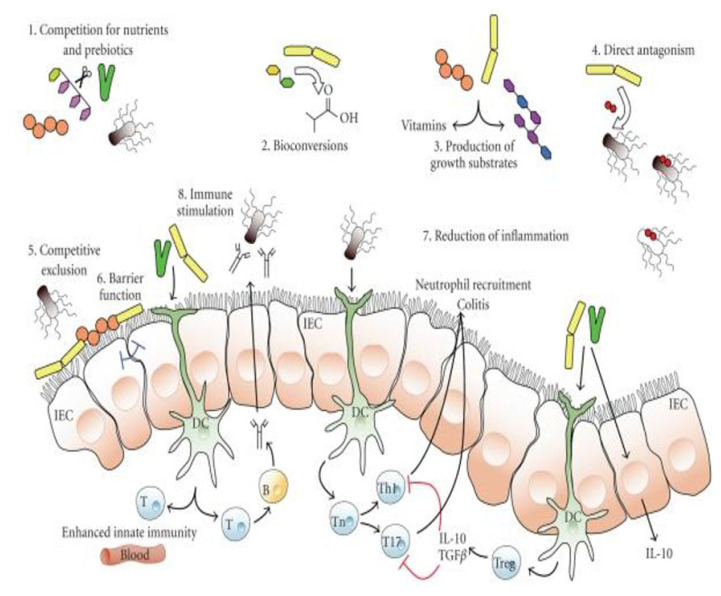
Figure 2.
Diagram showing the potential impact of probiotic bacteria on microbiota. The schematic diagram showing mechanism: 1) competition for nutrients and prebiotics for growth, 2) bioconversion of nutrients into other substances with selective inhibitory properties against pathogens, 3) production of growth substances like vitamins for other bacterial organisms, 4) direct antagonism through antibacterial agents like bacteriocins, 5) competitive exclusion for binding sites, 6) barrier function, 7) lessening of inflammation, hence changing intestinal ecosystem for colonization, and 8) modulation of innate immunity. IEC, epithelial cells; T, T-lymphocytes; B, B-lymphocytes; DC, dendritic cells; T, T-cells; Th1, T helper type 1; T17, a subset of T helper cell that produce interleukin 17; Treg, T-regulatory cell; IL-10, interleukin 10; TGFβ, transforming growth factor beta (adopted from https://www.customprobiotics.com/mechanisms-of-action ).