Fig. 4. VDR-specific deletion in mouse intestines lead to decreased Claudin-5 expression in tumor tissues.
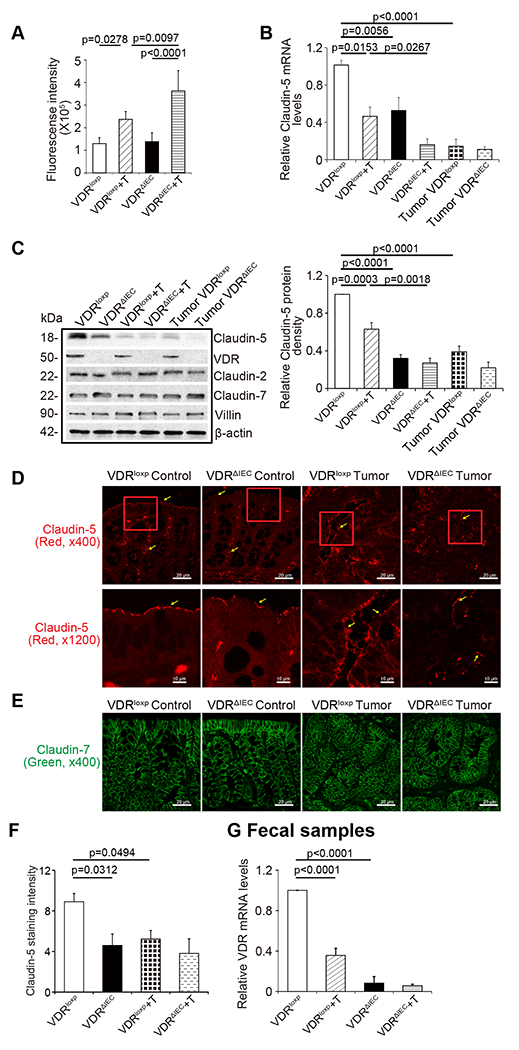
(A) Intestinal permeability was increased in the AOM-DSS-induce VDRΔIEC mice colon cancer model (data are expressed as mean ± SD; n = 5 mice/group, One-way ANOVA test). (B) VDR-specific deletion in mouse intestines decreased Claudin-5 at the mRNA level in the colon (data are expressed as mean ± SD. n = 5, one-way ANOVA test) (C) VDR-specific deletion in mouse intestines decreased Claudin-5 protein in the colon (data are expressed as mean ± SD. n = 5, one-way ANOVA test.) Claudin-2 was decreased in the VDRΔIEC mice, compared to the VDRloxp mice in the basal level, but not decreased in the tumor tissue of VDRΔIEC and VDRloxp mice. (D) Claudin-5 was decreased in the tumor tissue of VDRΔIEC mice compared to levels in the tumor tissue of VDRloxp mice according to immunofluorescence staining. Images are from a single experiment and represent 6 mice per group. (E) Claudin-7 expression was not changed in the AOM-DSS-induced VDRloxp mice colon cancer model. Images are from a single experiment and represent of 6 mice per group. (F) Intensity of the staining of Claudin-5. (Data are expressed as mean ± SD. n = 6, one-way ANOVA test). (G) VDR level in fecal samples was detected by RT-PCR. VDR expression was downregulated in the AOM-DSS-treated VDRloxp mice (data are expressed as mean ± SD. n = 3, one-way ANOVA test). All p values are shown in the figure.
