Figure 1.
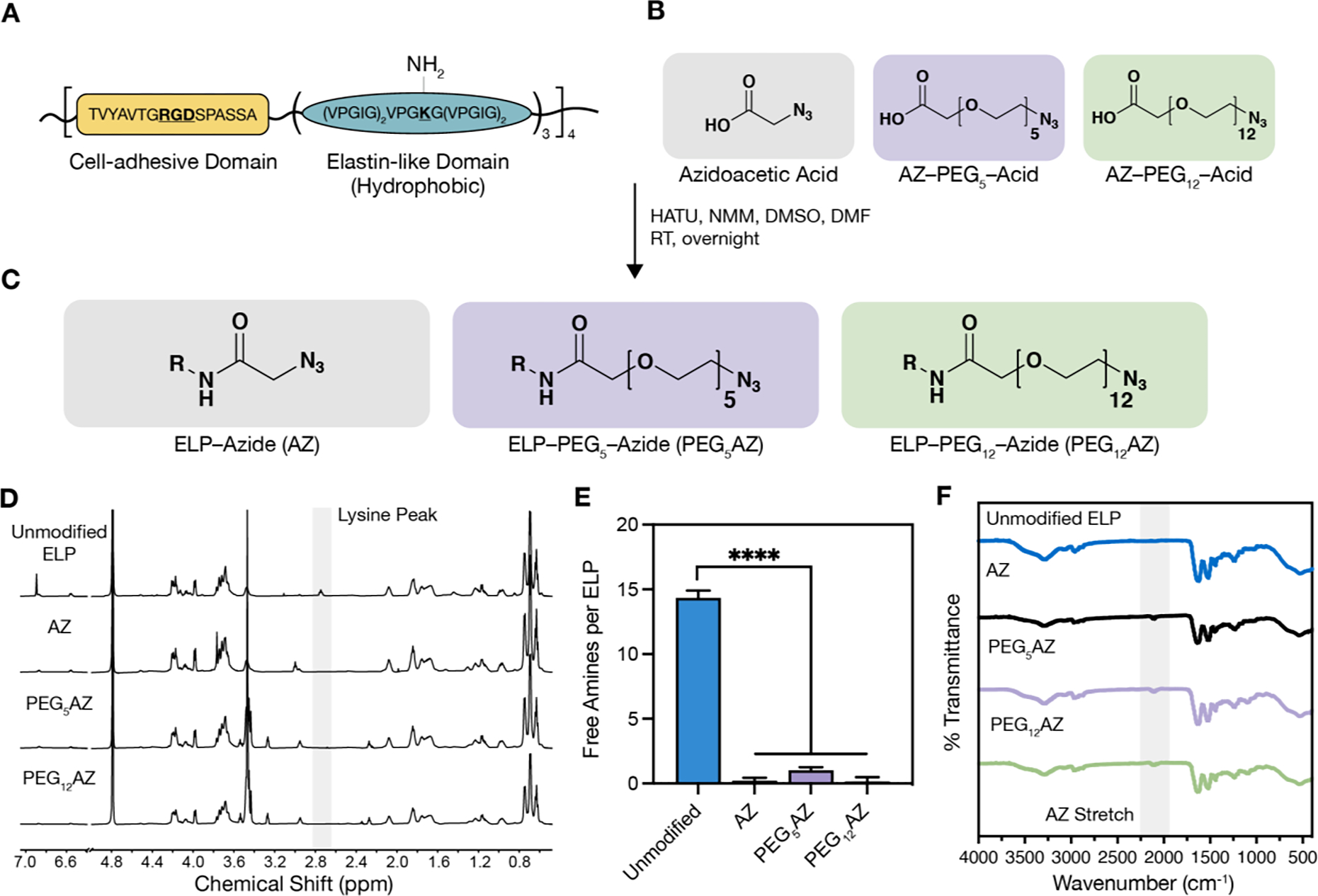
Schematic and characterization of azide-modified ELP. A) Amino acid sequence of ELP cell-adhesive domain and elastin-like domain, which contains the lysine amino acid (K) used for coupling to azide-containing molecules. B) Azide-containing molecules with increasing hydrophilicity from left to right. C) Reaction conditions and products for each of the resulting azide-modified ELPs; R = ELP. D) NMR spectra (600 MHz in D₂O) of azide-modified ELPs demonstrate a decreased peak at 2.75 ppm attributed to reaction of the primary amine side chain on lysine residues. E) Quantification of unmodified amines on ELP before and after coupling reaction (n = 3, data are averages ± standard deviation, ****p < 0.0001, one-way ANOVA with Tukey post hoc test). F) FTIR observation of azide functional group stretching (~2100 cm−1) before and after coupling reactions. HATU, hexafluorophosphate azabenzotriazole tetramethyl uronium; NMM, 4-methylmorpholine; DMSO, dimethyl sulfoxide; DMF, dimethylformamide; RT, room temperature.
