Figure 2. Characterization of act. caspase-1+ Tfh cells.
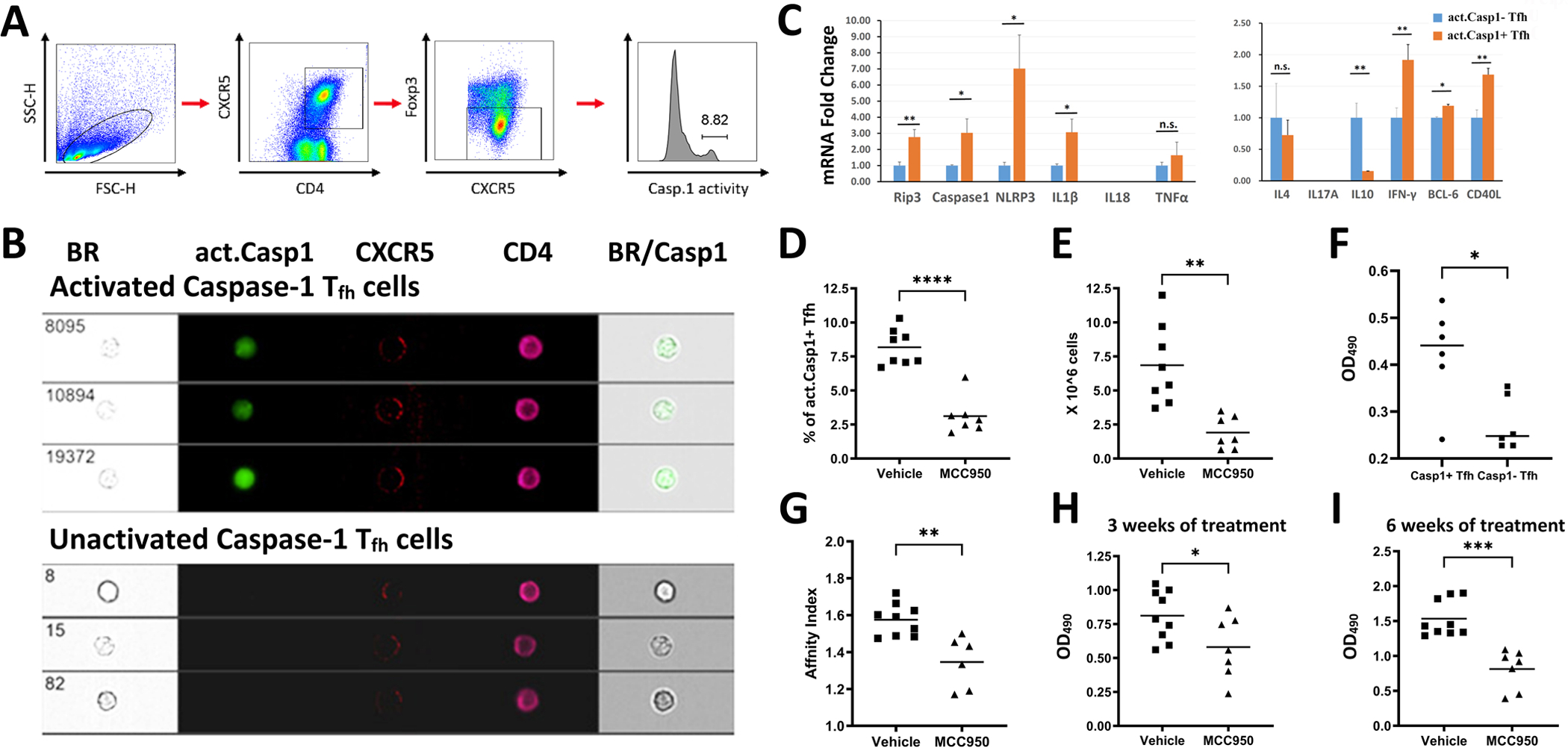
B6 mice were immunized with sheep Red Blood Cells (sRBC) as described in Methods. (A) Gating strategy for Tfh cells: Lymphocytes were gated by forward light scattering. CD4+CXCR5+ and FoxP3− cells were selected as Tfh cells. (B) The Tfh cells were sorted into act. caspase-1+ and act. caspase-1− cell populations. (C) mRNA expression of genes of interest in act. caspase-1+ Tfh and act. caspase-1− Tfh cells isolated from the spleens of immunized mice were interrogated by RT/PCR. (D) Act. caspase-1+ Tfh cells were elevated in the spleen of mice immunized with sRBC. This increase was inhibited by MCC950. (E) Total lymphocyte counts in the lymph nodes of immunized mice were decreased with MCC950. (F) Act. caspase-1+ Tfh cells provided better help to induce IgG secretion by B cells in comparison with act. caspase-1− Tfh cells. (G) MCC950 or vehicle treatment commenced five days after the second immunization, reduced affinity maturation to sRBC. Reduction of serum IgG anti-sRBC Ab in mice treated with MCC950 at three weeks (H) and at six weeks (I) after the secondary immunization. *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001 and ****p<0.0001.
