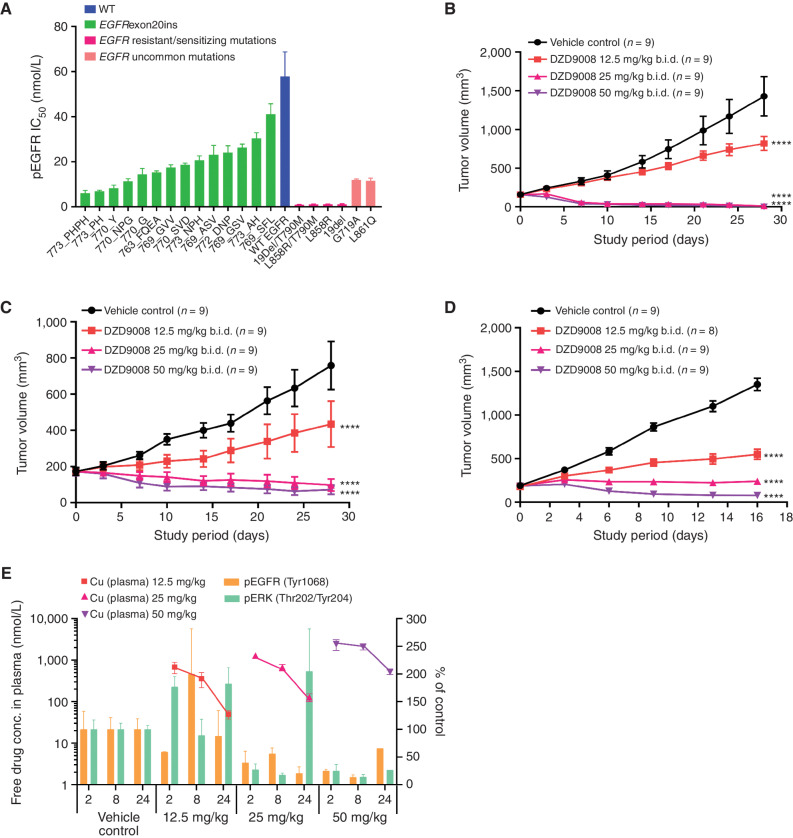
Figure 2.
In vitro and in vivo antitumor activity of sunvozertinib in EGFRexon20ins, sensitizing mutation, uncommon mutation, or resistant mutation cell lines and animal models. A, The cellular activity of sunvozertinib on EGFRexon20ins as well as sensitizing mutation, uncommon mutation, or resistant mutation versus wild-type (WT) EGFR, shown as pEGFR IC50. Cell lines carrying EGFRexon20ins were treated with sunvozertinib at a series of concentrations for 4 hours, and then pEGFR (Tyr1068) was measured with an MSD SECTOR Imager. In the A431 cell line carrying wild-type EGFR, after compound treatment for 4 hours, cells were stimulated with 100 ng/mL of recombinant human EGF for 10 minutes before lysis. The potency in each cell line was the average value from three biologically independent experiments. Data, mean ± SEM. One-way ANOVA test was used for comparison with wild-type EGFR. ****, P < 0.0001. B, Antitumor activity of sunvozertinib in the PDX model LU0387 carrying EGFRexon20ins insNPH. b.i.d., twice daily. C, Antitumor activity of sunvozertinib in the PDX model LU3075 carrying EGFRexon20ins 772_DNP. D, Antitumor activity of sunvozertinib in the A431 xenograft model expressing wild-type EGFR. Tumor volume in the different treatment groups at the endpoint was performed by two-way ANOVA. ****, P < 0.0001. E, PK/PD relationship of sunvozertinib in the PDX LU3075 model. The pEGFR (Tyr1068) and pERK (Thr202/Tyr204) expression in tumor tissues was detected by IHC and normalized to the vehicle control group. Each time point had tumor tissues from three mice to detect pEGFR or pERK signal except the time point of 24 hours in the 50 mg/kg group, which included only one mouse due to complete remission of tumor nodules in some mice. conc., concentration; pERK, phosphorylated ERK. DZD9008 = sunvozertinib.