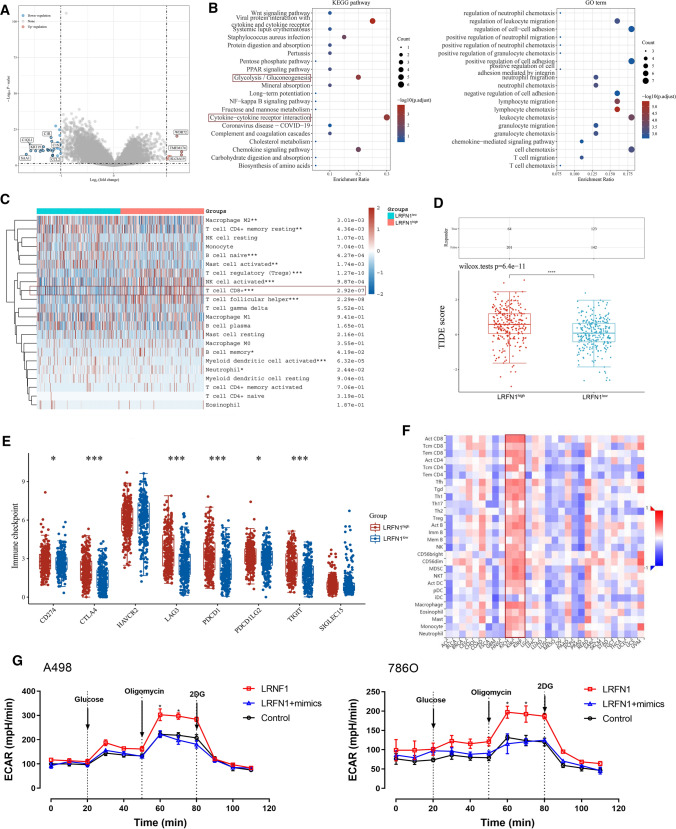
Fig. 5.
LRFN1 promotes immune-infiltrated TIME and aerobic glycolytic effects of ccRCC. A Limma R package was performed to identify the significant DEGs according to LRFN1 expression. B KEGG and GO functional enrichment analysis suggested that the LRFN1-related DEGs prominently involved in the hallmarks associated with tumorigenesis and progression. C CIBERSORT algorithm was performed to characterize immune cell composition of complex tissues from their gene expression profiles of ccRCC based on transcriptome data from TCGA database. D TIDE algorithm was performed to measure intratumoral heterogeneity of ccRCC with Student’s t test. E Expression of immune checkpoints were assessed using unpaired t test. F Association between LRNF1 expression and the infiltration of tumor immune-infiltrating lymphocytes in pan-cancer was assessed using Spearson’s correlation analysis. G ECAR of ccRCC cells were analyzed by a Seahorse XFe 96 Extracellular Flux Analyzer. All results are representative of at least three independent experiments. Asterisk represents significant differential ECAR value between LRNF1 overexpression group and negative control group, as well as between LRNF1 overexpression group and LRFN1 + mimics group using unpaired t test (P < 0.05). *P < 0.05; ***P < 0.001; ****P < 0.0001