Figure 1.
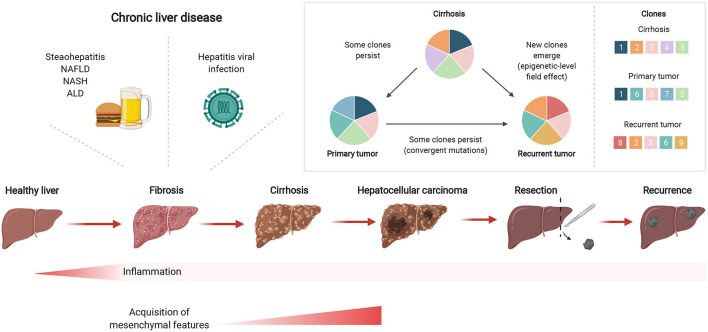
Chronic liver inflammation predisposes potential genetic changes for selective clonal expansion during HCC development. Inflammation triggered by chronic liver diseases, such as fatty liver disease or hepatitis viral infections, can eventually develop into fibrosis which can subsequently lead to cirrhosis. In cirrhotic tissues, hepatocarcinogenesis is a multistep process whereby the repeated cycles of cell damage and hepatocyte regeneration may predispose the accumulation of various multi-omic changes. Therefore, this chronic inflammatory microenvironment sets up a scenario that promotes the hepatocytes with an advantageous mutational burden for clonal expansion and eventually selects for HCC lesions. Created with www.BioRender.com.